Topic Content:
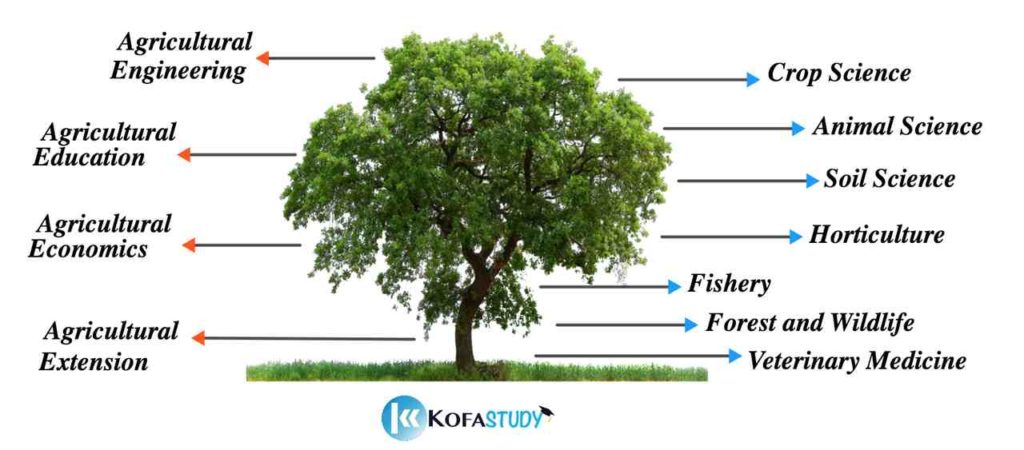
- Branches/Areas of Agriculture
Here are the main Branches of Agriculture:
- Crop Science.
- Animal Science.
- Soil Science.
- Horticulture.
- Fishery.
- Forestry and Wildlife.
- Veterinary Medicine.
- Agricultural Engineering.
- Agricultural Education.
- Agricultural Economics.
- Agricultural Extension.
1. Crop Science:
This is the study of how crops are grown and used by man and animals. It gives the farmer the knowledge of how crops are grown, from planting to harvesting and storage. The farmer uses this knowledge to take care of the crops. One who studies crop science is called a crop scientist. Areas of crop science include:
Plant breeding: Plant breeding is the art and science of improving important agricultural plants for the benefit of humankind.
Agronomy: Agronomy is the science and technology of producing and using plants by agriculture for food, fuel, fiber, chemicals, recreation, or land conservation.
Pathology: Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions.
Entomology: Agricultural entomology is a subdivision of Entomology which is the study of pests and beneficial insects of field crops, fruits and vegetables.

2. Animal Science/Animal Husbandry:
Animal science, also known as Animal husbandrythe care, cultivation, breeding and production of crops and animals. More, deals with the study of the production of farm animals which are called livestock. These farm animals include sheep, poultry, cows, sheep, fish, pigs, rabbits, etc. Farm animals are of great importance to any economy because they supply milk, meat, and eggs which are important protein sources, while their hides and skin are used to make clothes, leather, etc. One who studies animal science is called an animal scientist.

3. Soil Science:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses