Quiz Summary
0 of 5 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 5 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 5
1. Question
(a) State four reasons why animals move from one place to another.
(b) Mention one function each of the following structures in plants:
(i) Phloem
(ii) Leaf
(iii) Xylem
(iv) Flower
(c) Describe three features of plants in desert habitat.
(d) (i) Explain the process of image formation in the human eye.
(ii) List three evidences of organic evolution.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 2 of 5
2. Question
(a) List two structures that protect the eyes.
(b) Define the following:
- Excretion
- Competition
- Deforestation
(c) Draw a well labeled diagram (8 – 10m long) of the thoracic vertebra of a named mammal.
(d) State four methods of preventing food spoilage.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
Question 3 of 5
3. Question
(a) State the number of daughter cells produced in:
- Meiosis
- Mitosis
(b) (i) Mention three importance of sexual reproduction
(ii) Describe the relationship between remora fish and shark in their habitat.
(c) (i) State three symptoms of covid-19.
(ii) State one function of the renal vein in mammals.
(d) Write short notes on each of the following:
- Ecological niche
- Population density
- Climax community
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
Question 4 of 5
4. Question
(a) (i) Define aestivation.
(ii) List four sense organs and one function of each.
(iii) Describe the process that makes a person who has been spinning round a stationary object to feel dizzy.
(b) State one function each of the following structures:
– Neuron
– Cerebrum
– Medulla oblongata
– Cerebellum
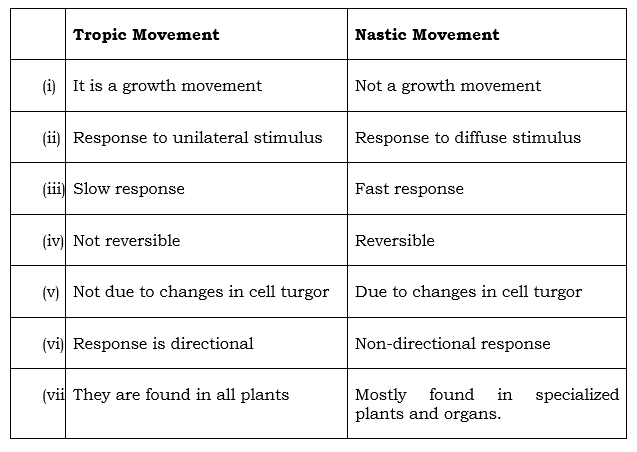
(c) (i) In a tabular form, give three differences between tropic and nastic movements.
(ii) List three adaptive features of a leaf to photosynthesis.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 5 of 5
5. Question
(a) (i) Describe the courtship behaviour display in Agama Lizard.
(ii) Name four examples of sex-linked trait in man.
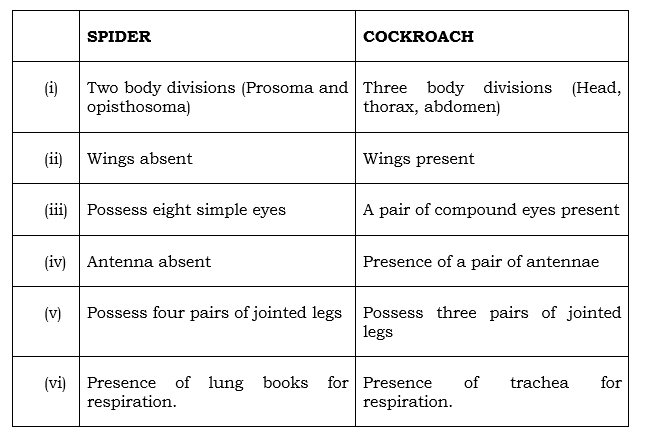
(iii) In a tabular form, enumerate three differences between spider and cockroach.
(b) By means of crosses, show how children could inherit sickle cell anaemia from parents who are carriers. Use SS to indicate normal gene and ss
What ratio of F1 generation would be?
(i) Sickler
(ii) Carrier
(iii) Normal
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -





Thanks for putting these questions here for teachers use