WAEC: ECONOMICS
Quizzes
-
2021 Economics WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2021 Economics WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2020 Economics WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2020 Economics WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2019 Economics WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2019 Economics WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2018 Economics WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2018 Economics WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2017 Economics WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2017 Economics WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2016 Economics WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2016 Economics WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2015 Economics WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2015 Economics WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2014 Economics WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2014 Economics WAEC Theory Past Questions
Quiz Summary
0 of 8 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 8 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 8
1. Question
The diagram below represents the equilibrium position of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow

a (i) At what level of output and prices is the firm in equilibrium?
(ii) Calculate the firm’s profit in equilibrium
(iii) What type of profit is it? Explain your answer
(b) Why is the average revenue (AR) function horizontal
(c) State any two ways in which marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) are related
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 2 of 8
2. Question
The extract from a country’s balance of payments account is shown below
ITEMS IMPORT ($million) EXPORT ($million) Agricultural products – 200 Mineral resources – 300 Consumer goods 250 – Capital goods 400 – Insurance 50 25 Banking 75 30 Transportation 85 25 Loans 150 60 Using the table above, calculate the
(a) balance of trade
(b) Invisible trade
(c) balance on current account
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 3 of 8
3. Question
a(i) Define distribution of goods
(ii) Illustrate the normal chain of distribution of goods
(b) Describe a consumer’s cooperative society
(c) Outline any four roles performed by a consumers’ cooperative society
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 4 of 8
4. Question
(a) What is an industry?
(b) Explain the following
(i) Division of labour
(ii) Economies of scale
(c) Outline any four internal economies of scale
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 5 of 8
5. Question
(a) Define a joint venture
(b) Identify any three merits of a private company over a partnership
(c) State any three sources of finance to a public enterprise
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 6 of 8
6. Question
(a) Distinguish between the following pairs of concepts
(i) Elastic demand and Inelastic demand
(ii) Income elasticity of demand and cross elasticity of demand
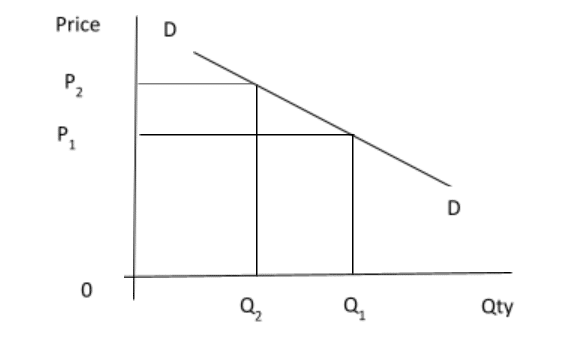
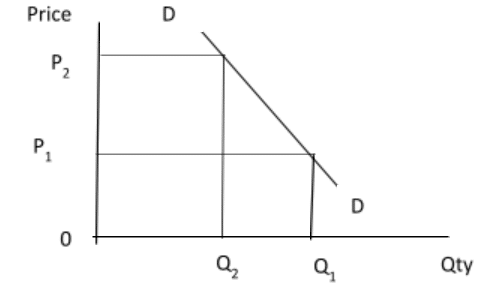
(b) Using diagrams, explain how an increase in demand will affect total revenue of a producer if demand for his product is
(i) Price elastic
(ii) Price inelastic
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 7 of 8
7. Question
(a) Distinguish between
(i) Growing population and a declining population
(ii) Overpopulation and underpopulation
(b) Explain any four disadvantages of a rapidly growing population in an economy
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 8 of 8
8. Question
(a) What is public debt?
(b) Outline any three reasons why countries borrow
(c) Highlight any three effects of huge national debt on the economy of a country
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -






Responses