Topic Content:
- Changes of States of Matter
All matter is interchangeable, that is it can change from one state to the other, as a result of a change in temperature.
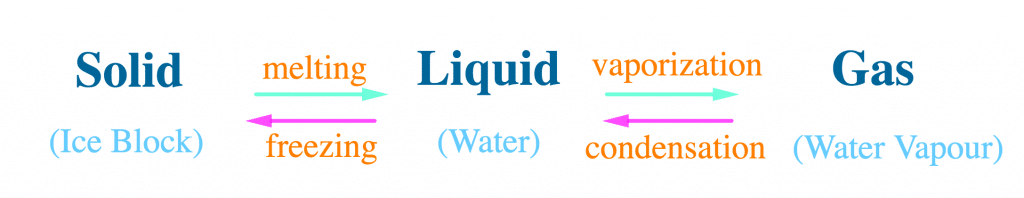
Melting:
When a solid changes into a liquid, it is called melting, for example, ice to water. The temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid is called “melting point”.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



EVALUATION
What is matter?
Matter is a substance on which objects are made
List 3 state of matter?
1. gas 2. liquid 3. solid
Give one example of change of state in matter
Melting
What is classification?
Classification is when we classify matter in shapes, sizes, color, taste, and appearance
matter is a substance that has weight and contains space and made
1.gas 2.liquid 3. solid
melting
a group of something
solid- melting- liquid- vapourization-gas
no