Topic Content:
- Exterior and Interior Opposite Angles
In triangle XYZ below on the left (Fig. 9.2.1), the exterior angle is “a” and the two opposite interior angles are x and y.
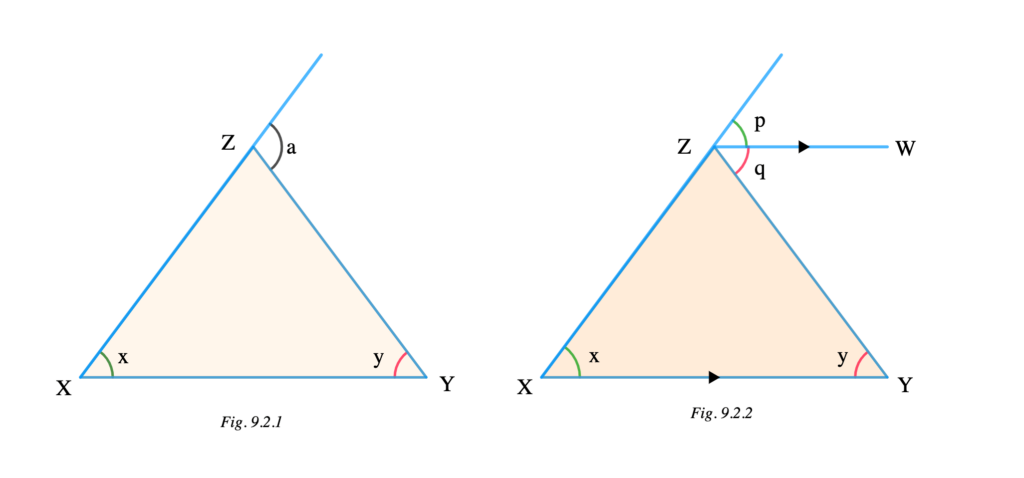
To prove that a = x + y:
Draw a line at Z (i.e. line ZW) to divide the exterior angle “a” into angles p and q and let this line be parallel to line XY (see Fig. 9.2.2).
∴ a = p + q ……….(1)
From the diagram on the right (Fig. 9.2.2),
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Easy subject