Topic Content:
- Classes of Chemicals Based on Uses
- Pharmaceutical/cosmetics, Nuclear, Agrochemical, Industrial, Laboratory
Chemicals can be classified based on their use;
a. Pharmaceutical / Cosmetics:
i. Pharmaceutical Chemicals:
These are substances that have the power to heal certain diseases. They are substances used in the diagnosis, treatment, or prevention of disease and for restoring, correcting, or modifying organic functions.
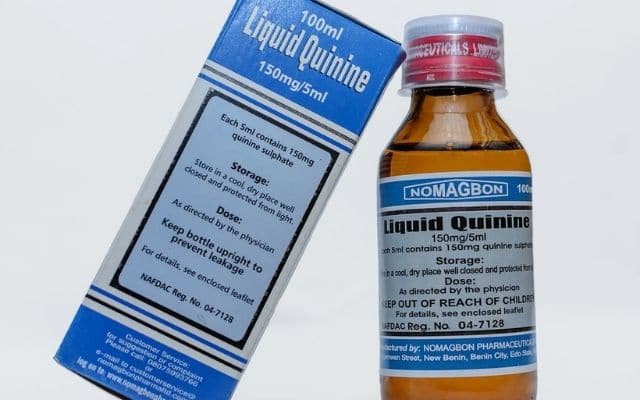
Examples of pharmaceutical chemicals are as follows:
1. Bismuth Trioxocarbonate (IV) is used to cure stomach disorders.
2. Potassium bromide: used as a sedative.
3. Quinine: For treatment of malaria fever.
4. Mercury (I) Chloride: Used as a purgative.
5. Insulin: For treatment of diabetes.
6. Aspirin: Used as a pain reliever.
ii. Cosmetic Chemicals:
These are chemicals used in beauty products like soaps, creams, etc. examples are:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses