Topic Content:
- Definition of Ledger
- Classification of Ledger Accounts
- Personal Ledger
- Impersonal Ledger
- Items on the Ledger
- Common Abbreviations used in the Ledger
What is a Ledger?
The ledger is the main book of accounts used for recording all accounting transactions. In the ledger, financial transactions are posted using the double-entry system.
Division of Ledger:
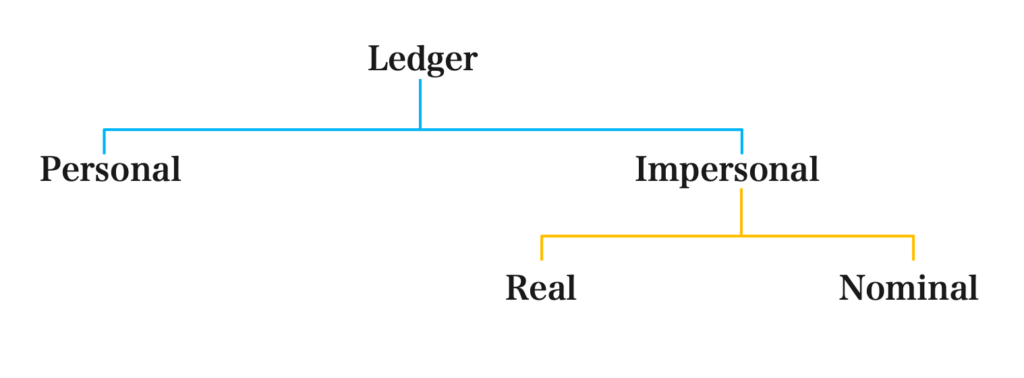
Ledger Classification:
Personal Ledger:
The personal ledger is used for recording accounts with names of individuals, firms, or organizations who may either be customers or suppliers. An example of a personal ledger is a capital account, which is an account where the entrepreneur’s investment in the business is recorded.
Impersonal ledgers:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Will love to be part of this website
helped me in exams thanks a lot friend me