Topic Content:
- Meaning of Standard Index Form
- Standard Index Form of Numbers Greater than 1
What is Standard Index Form?
Standard index form or Standard form is a way of expressing numbers as a product of two terms: The first term is a number between 1 and 10 and the second part is a power of 10.
In general, it is expressed as \( \scriptsize \; a \; \times \; 10^n \!\!\;\)where a is a number between 1 and 10 and n is an integer which can be positive, negative or zero.
Numbers Greater Than 1:
Every number has a decimal point usually at the back of the last digit of the number. E.g. 15, the decimal point is after 5. Also, 706 the decimal point is after 6.
Worked Example 7.1.1:
Express these numbers in standard form:
a. 25 000 000
b. 5 000
c. 7
d. 270 000
e. 15
Solution
a. 25 000 000
Step 1: Move the decimal point to the back of the first significant digit
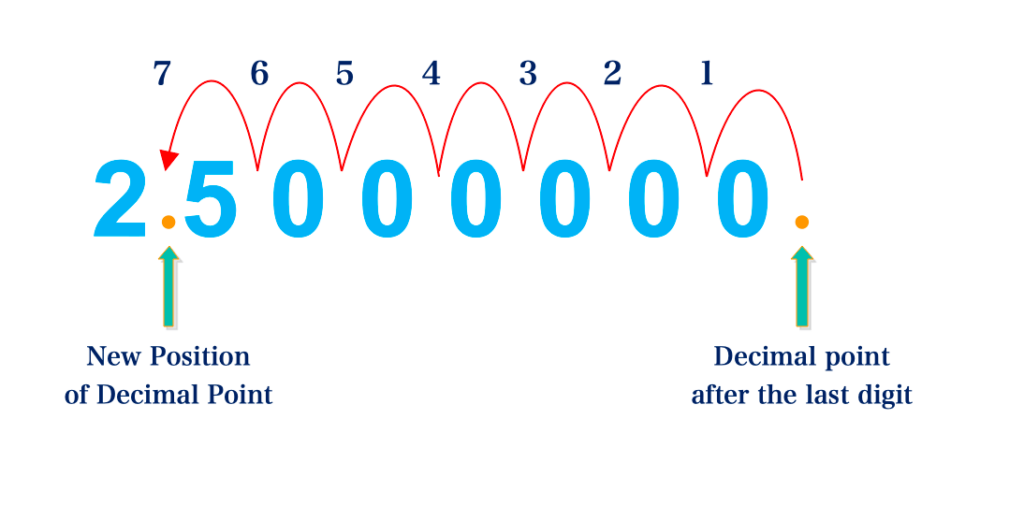
Step 2: Count the number of movements made from the initial position of the decimal point.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses