Topic Content:
- Ozone Layer
- Natural Production of Ozone
- Importance of Ozone layer

The atmosphere is comprised of layers based on temperature. These layers include the
- troposphere
- stratosphere
- mesosphere
- thermosphere
- exosphere
Exosphere is the outermost layer (very edge) of the atmosphere. It extends from about 440 miles (700 km) to 6,200 miles (10,000 km ) above the earth. In this layer, atoms and molecules escape into space and satellites orbit the earth.
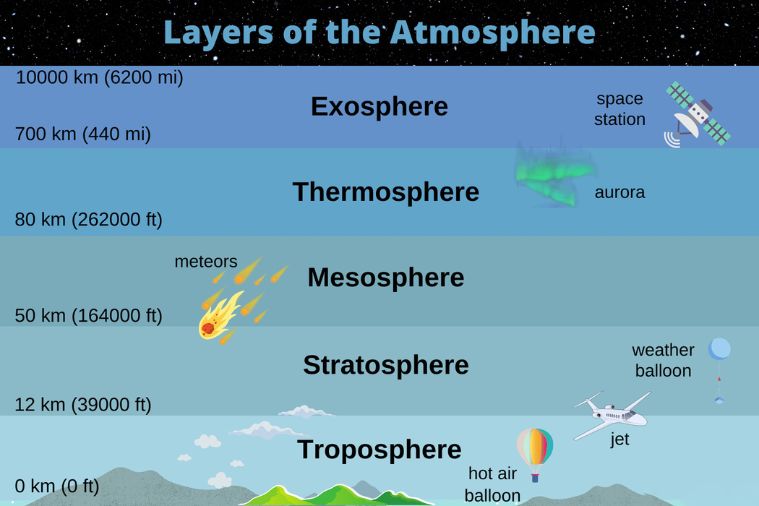
The ozone layer, 15 to 30 km above the earth’s surface, is located in the lower stratosphere, which is the second layer of the earth’s atmosphere. The stratosphere starts just above the troposphere and extends to 50 km (31 miles) high, with its highest concentration at about 25 km above the ground.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses