Question 1 ( No. 12. 2022 Physics WAEC Theory Past Question)
(a)(i) What is meant by the term artificial radioactivity?
(ii) Complete the table below.
| Emission | Nature | Charge | Ionizing-ability |
| High speed electron | Moderately ionizing | ||
| Neutral | Negligible ionizing ability | ||
| Alpha particle | Positive |
(b) In an x-ray tube, an electron is accelerated from rest towards a metal target by a 30 kV source. Calculate the kinetic energyEnergy is the ability to do work. Energy exists in several forms such as heat, kinetic or mechanical energy, light, potential energy, and electrical energy. Units of Energy: The SI unit... More of the electron. [e = 1.6 × 10-19 C]
(c) The table below shows the frequencies of radiations incident on a certain metal and the corresponding kinetic energies of the photoelectrons.
| Frequency × 1014 (Hz) | 6.8 | 8.0 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 11.0 |
| Kinetic energy × 10-19 (J) | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 3.8 |
(i) Plot a graph of kinetic energy, K.E, on the vertical axis and frequency, f, on the horizontal axis starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
(ii) From the graph, determine the:
I. Planck’s constant;
II. Threshold frequency of radiations;
III Work function of the metal.
Question 2 ( No. 9. 2022 Physics WAEC Theory Past Question)
(a)(i) State Coulomb’s law of electrostatics.
(ii) The electron and proton of a hydrogen atom are separated by a mean distance of \( \scriptsize 5.2 \: \times \: 10^{-11} \: m\)
Calculate the magnitude of the electrostatic force between the particles.
[e = 1.6 × 10-19 C, (4πε0)-1 = 9.0 × 109 mF-1]
(b)(i) The diagram below shows a potential divider circuit.
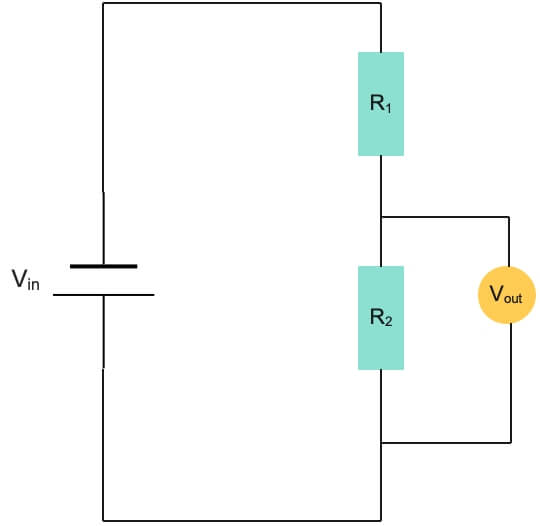
I. Show that Vout = \(\scriptsize V_{in} \left( \normalsize \frac{R_1}{R_1 \:+\: R_2}\right) \)
II. If \( \frac{V_{in}}{V_{out}}\) = 2.5 and R1 = 30Ω, calculate R2.
iii. Define the volt.
(c) Explain why wood is not suitable for use as the core of transformers.
(d) State one application for the cathodeA cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves the electrolyte. It is the negative part of the cell where reduction takes place. More ray tube.
View Solution



Responses