Topic Content:
- Characteristics of Phylum Platyhelminthes
- Classification of Platyhelminthes
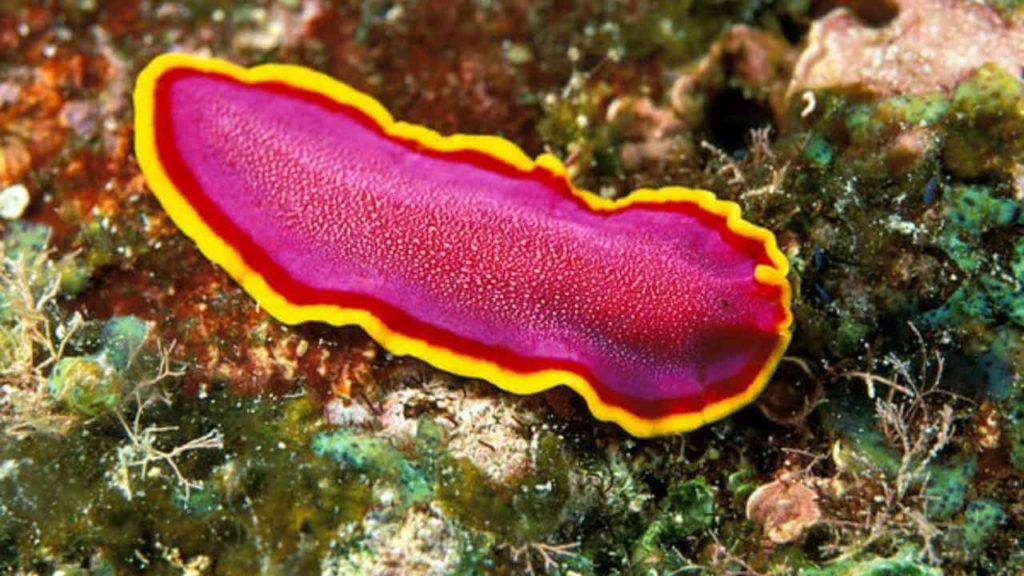

Phylum Platyhelminthes are also known as flatworms and they include many free-living and parasitic life forms.
Characteristics of Phylum Platyhelminthes:
Below are important characteristics of Platyhelminthes:
1. They are multicellular flatworms with tissues, organs and organ systems including a nervous system with a simple brain.
2. They are triploblastic with three body layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm)
3. They do not have a body cavity (acoelomates.)
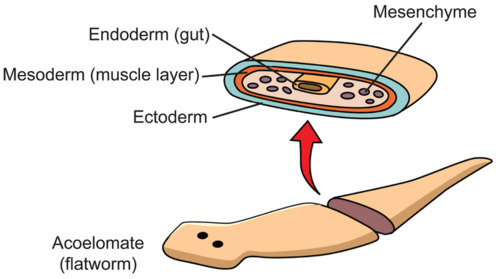
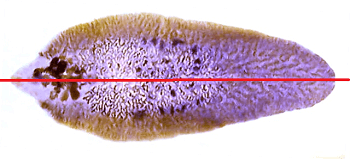
4. Their body is dorsoventrally flattened.
5. They exhibit bilateral symmetry. Bilateral symmetry is the arrangement of body parts into left and right halves on either side of a central axis.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses