Topic Content:
- Characteristics of Kingdom Protista
- Characteristics of Phylum Protophyta (Plant-like Protist)
- Characteristics of Phylum Protozoa (Animal-like Protists)
- Characteristics of Phylum Amoebozoa (Fungus–like Protist)
- Animal-Like Characteristics of Euglena
- Plant-like Characteristics of Euglena
Kingdom Protista:
Organisms in this kingdom are called protists. They are similar to plants, animals, and fungi but do not have the same characteristics as them. They can be divided into plant-like protists, animal-like protists and fungus-like protists.
Characteristics of Kingdom Protista:
1. They are all eukaryotes and single-celled or unicellular organisms.
2. They are usually aquatic, present in the soil or in areas with moisture.
3. Members of this kingdom move by various means: e.g. Amoeba uses Pseudopodia, Paramecium uses Cilia while Euglena uses Flagella.
4. They are microscopic organisms.
5. Mode of nutrition is variable: AutotrophicAn autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. It feeds itself, without the assistance of any other organisms. The word... More or HeterotrophicA heterotroph is an organism that consumes other organisms in a food chain. The term stems from the Greek words hetero for “other” and trophe for “nourishment.” More;
- Examples of heterotrophs are Amoeba and Paramecium.
- Examples of autotrophs are Euglena, Spirogyra, and Chlamydomonas.
6. They reproduce asexually by binary fission, multiple fission, spore formation, and budding.
7. They reproduce sexually by conjugation (a primitive form of sexual reproduction where individuals exchange genetic materials.)
- Examples are Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, etc.
8. Some cause serious diseases, such as malaria and amoebic dysentery
Phylum Protophyta (Plant-like Protist):
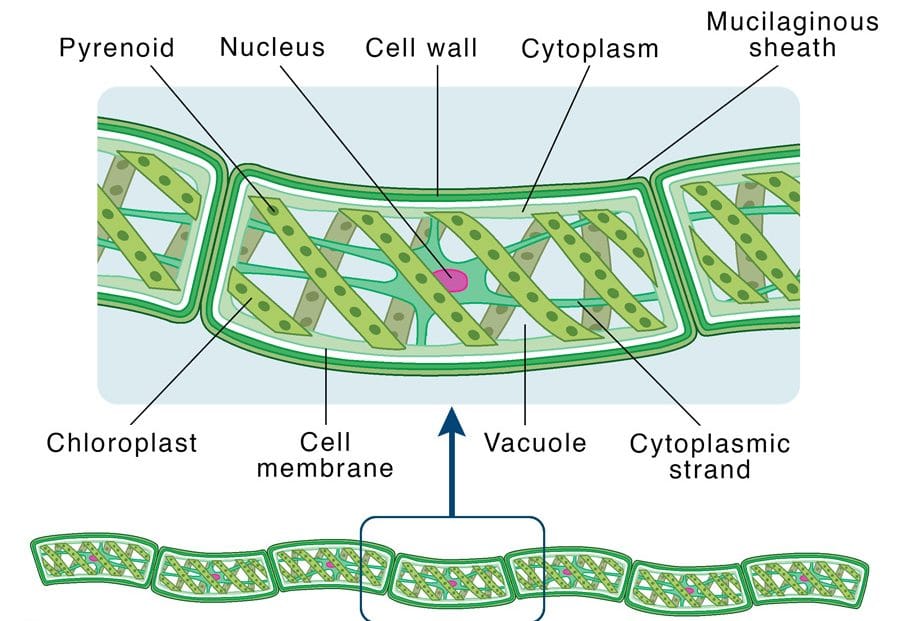
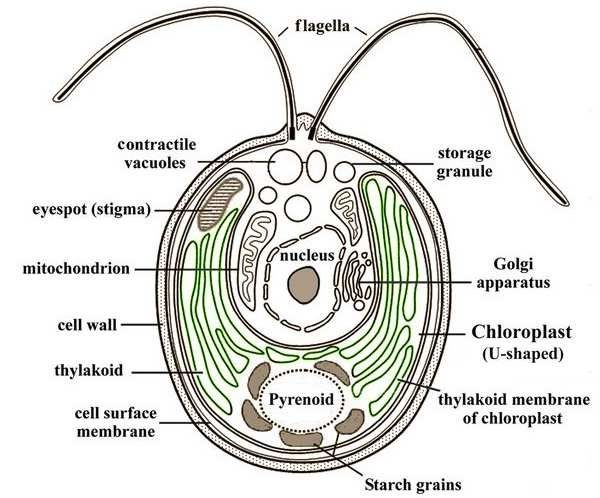
Plant-like protists are known as Protophyta e.g. Algae such as Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Chlorella, Volvox, Pandorina, and Diatoms.
Characteristics of Phylum Protophyta:
i. Possession of chloroplast.
ii. Autotrophic nutrition.
iii. Store Carbohydrates in the form of starch.
iv. Possess pyrenoid where starch is stored.
Phylum Protozoa (Animal-like Protists):
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses