Topic Content:
- Levels of Organisation
- cells
- tissues
- organs
- systems
- multicellular organisms
There are different levels of organisation of life e.g. cells, tissues, organs and systems.
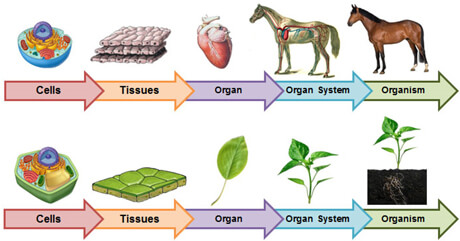
1. Cells:
The cell is the basic unit of a living thing capable of doing all life activities.
A cell can exist independently as a single-celled or unicellular organism or as a part of a multicellular organism.
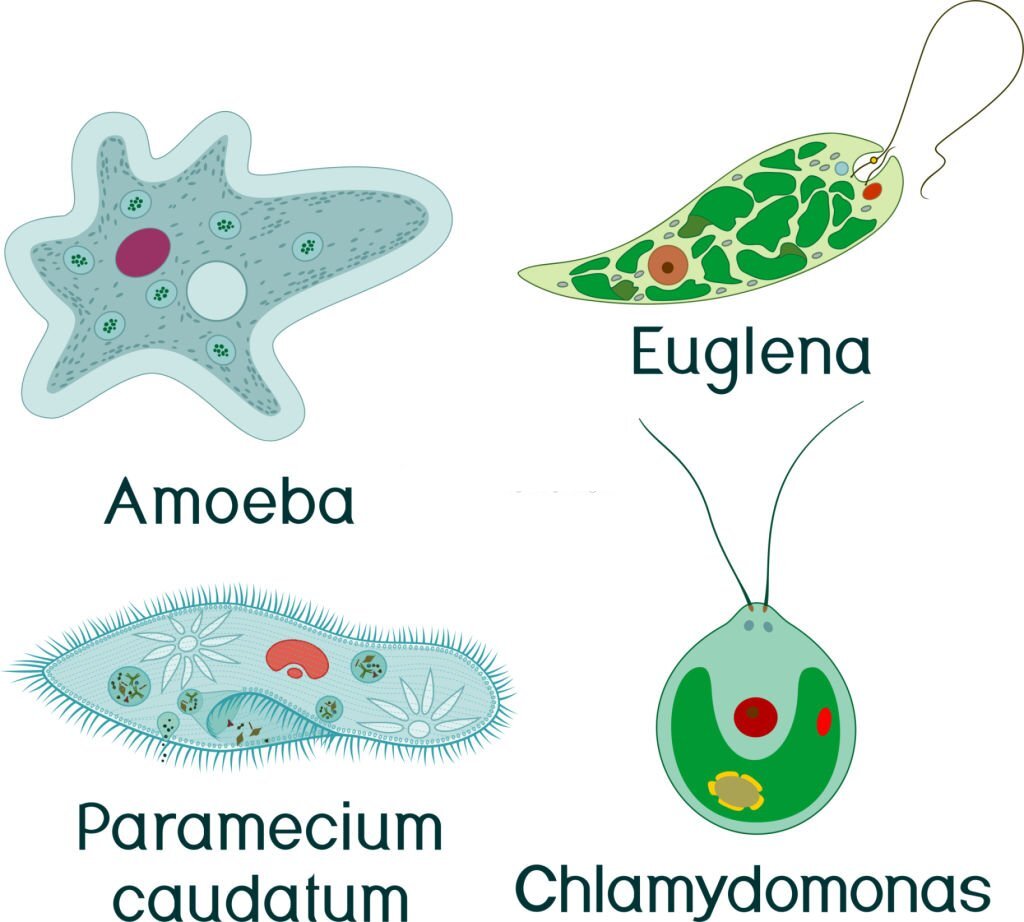
Examples of unicellular organisms are:
a. Amoeba
b. Paramecium
c. Euglena
d. Plasmodium
e. Trypanosome
f. Chlamydomonas
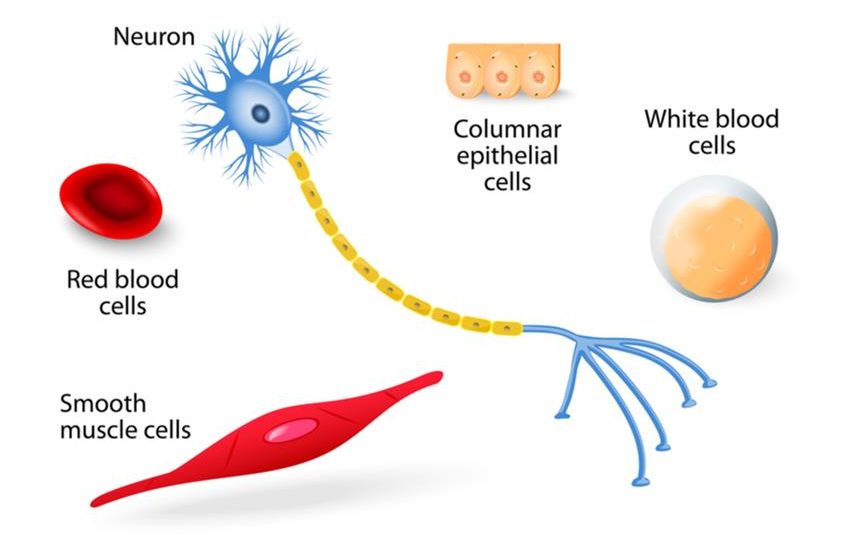
Examples of multicellular organisms are:
a. Blood cells
b. PhloemPhloem is a plant vascular tissue that conducts foods made in the leaves during photosynthesis, downwards to all other parts of the plant. More cells
c. Spermatozoa
d. Ova or eggs
e. Nerve cells
f. Epidermal cells
2. Tissues:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Nice study platform
This is a very good source. Thank you.
awesome description and presentation
I did a 4 month subscription and I can’t view the full notes. Please treat this now….
Are you sure you are logged in properly? Try and log in again.