Topic Content:
- The Cell Structure and Functions
Cells vary a great deal in size and shape depending on their function. Nevertheless, it is possible to make a drawing to show the generalized features of a cell, though there is no such thing as a typical plant cell or animal cell.
Generally, all cells have a cell membrane which is a thin layer of the cytoplasm. Most cells have a nucleus. The main cell organelles and their function are shown below.
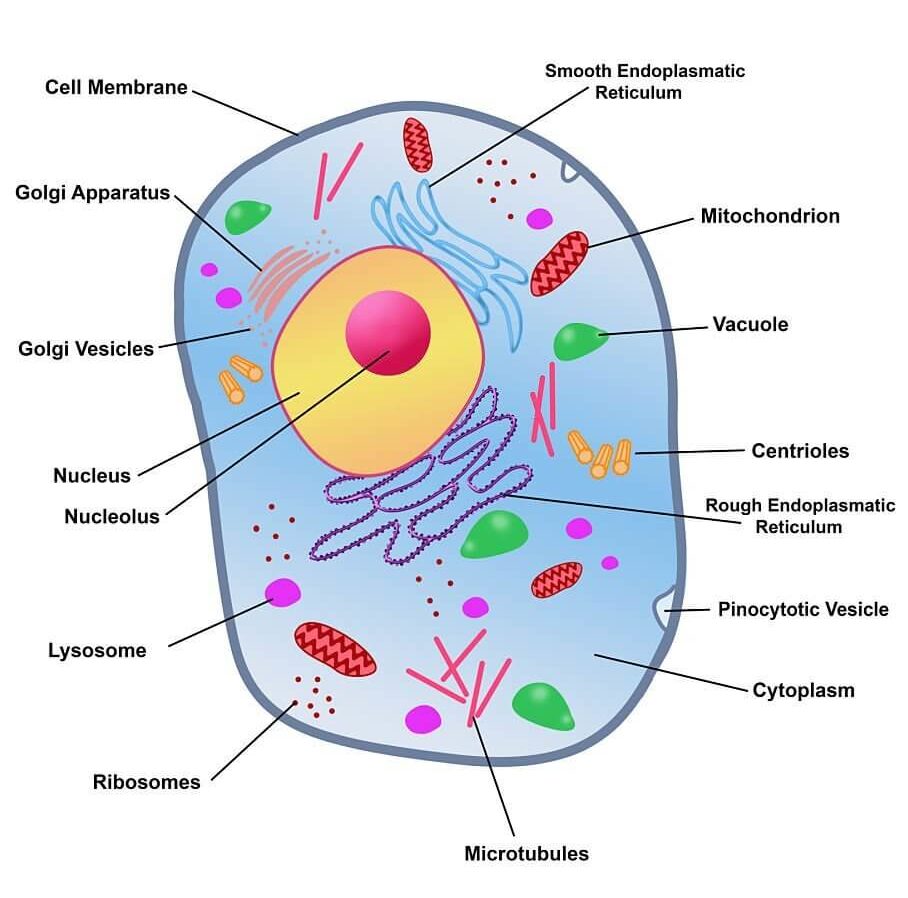
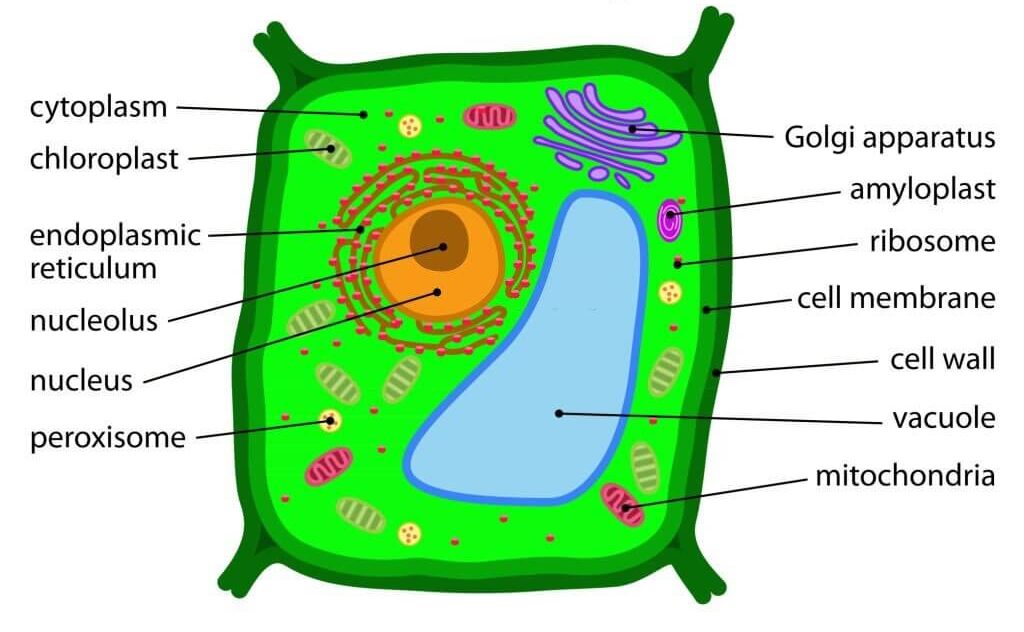
1. Nucleus:
Most cells contain one nucleus seen as a rounded structure enclosed in a membrane (nuclear membrane) and embedded in the cytoplasm. The nucleus contains chromosomes (made of DNA).
The nucleus is surrounded by a selectively/semi-permeable membrane that contains pores and allows for the transport of large molecules such as RNA.
Functions:
i. It controls the type and quantity of enzymes produced by the cytoplasm.
ii. The nucleus controls cell division.
iii. It controls and coordinates many activities of the cell.
2. Nucleolus:
Contained within the nucleus is a dense, membrane-less structure composed of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus.
There are tangles of chromatin and unfinished bits of ribosomes. They are prominent inside the nucleus of non-dividing cells.
Function: They are concerned with RNA transcription (copying of gene sequence to make an RNA molecule).
3. Cytoplasm:
It is a jelly-like material made up of cytoplasmic organelles such as Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. Organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm.
Function: Many chemical reactions take place here which keep the cell alive by providing energyEnergy is the ability to do work. Energy exists in several forms such as heat, kinetic or mechanical energy, light, potential energy, and electrical energy. Units of Energy: The SI unit... More and making substances that the cell needs.
4. Protoplasm:
This Is the living material inside the cell membrane. It is made up of the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
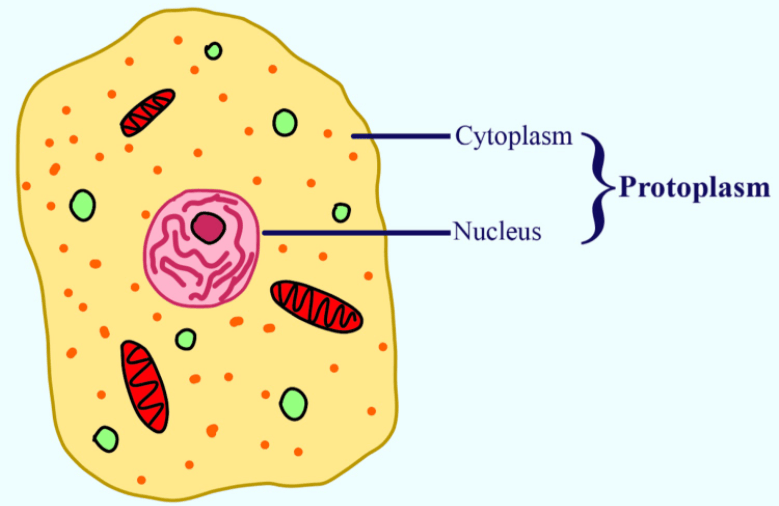
Functions:
i. Transforms food into living matter
ii. Removing waste products
iii. Provides nutrients and oxygen and renews worn-out parts.
iv. Helps in producing new cells.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses