Topic Content:
- Cells as Unicellular and Independent Organisms
- Cells as a Colony (e.g. Volvox, Pandorina)
- Cells as Filaments
- Cells as a Part of a Multicellular Organism
Cells of living organisms exist in different forms and they are;
- Unicellular/single and free-living
- As a colony
- As a filament
- As part of a living organism
1. Cells as Unicellular and Independent Organisms:
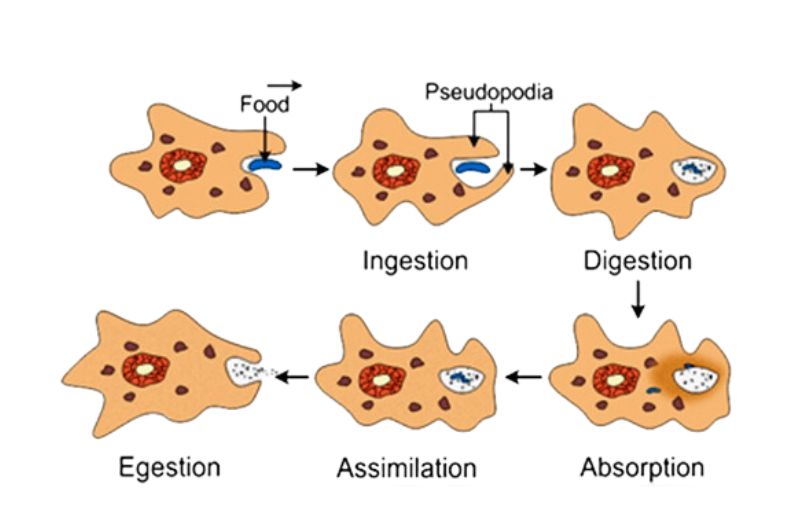
Unicellular organisms are organisms that have a single cell. These organisms are capable of living independently without depending on other cells e.g. Amoeba, Paramecium, and Euglena.
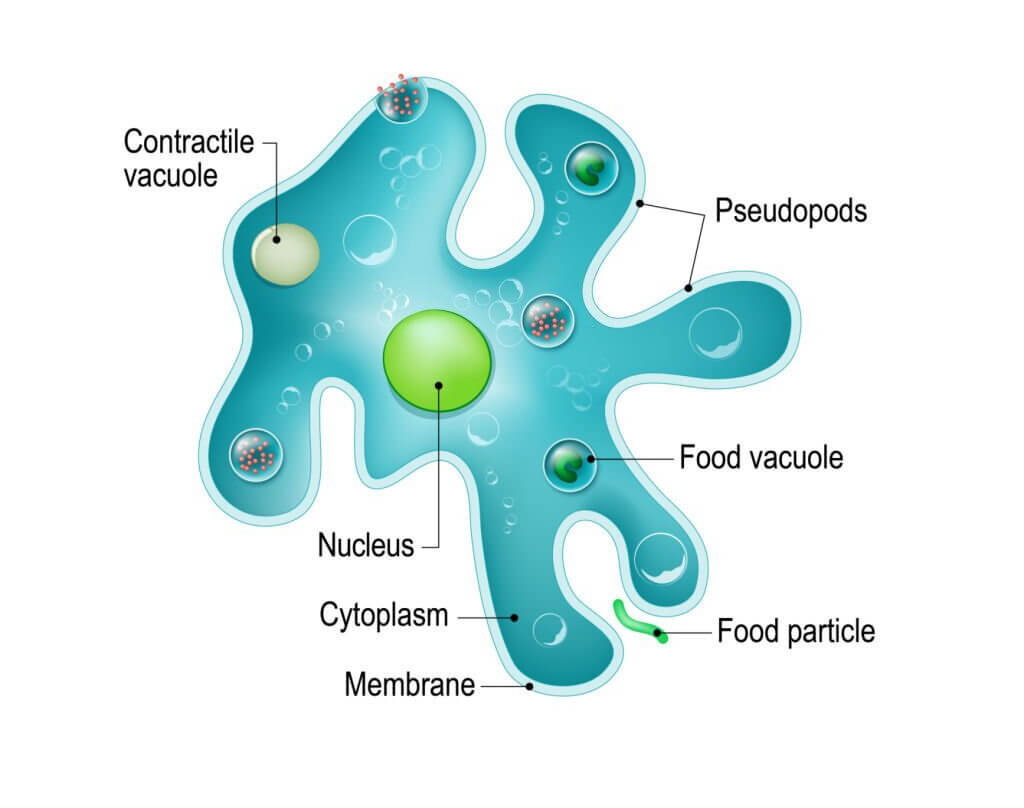
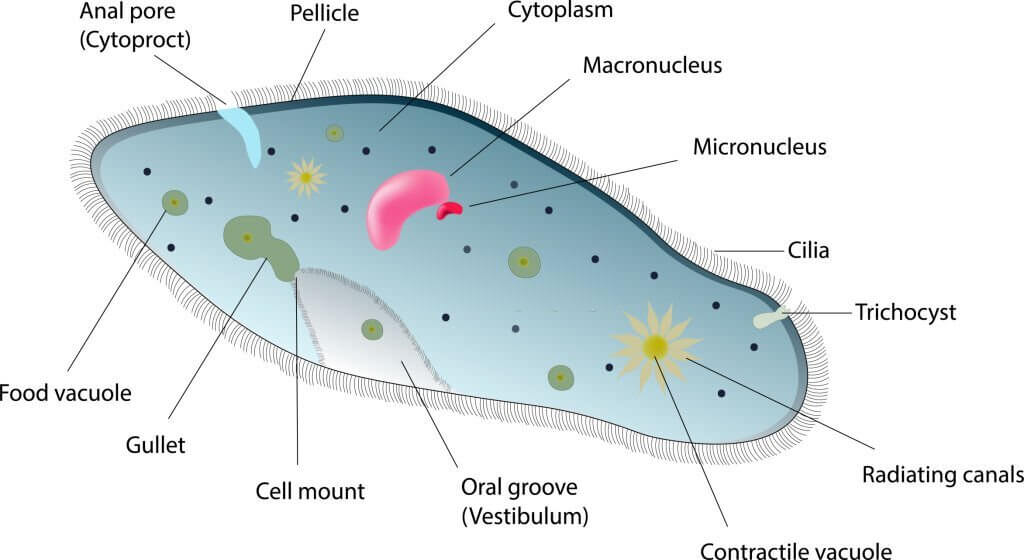
Each organism can carry out all life processes such as movement, growth, nutrition, reproduction, excretion, respiration, etc.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



It’s helpful
Thanks alot, this was so useful.
Thanks so much
It went a long helping me
thanks
i appreciate
Biology SS1 first term work
Thanks slot it is so helpful and useful
So helpful