Topic Content:
- Meaning of Covalent Bonding
- Formation of Chlorine molecule (Cl2)
- Formation of Hydrogen molecule (H2)
- Formation of Oxygen molecule (O2)
- Formation of Nitrogen Molecule (N2)
- Formation of Water Molecule (H2O)
- Formation of Ammonia (NH3)
- Formation of Methane (CH4)
- Formation of Carbon (IV) Oxide (CO2)
- Types of Covalent Bonds (Non-Polar Covalent Bond, Polar Covalent Bond)
- Factors that Determine Covalent Bonds
- Characteristic Properties of Covalent Compounds
Covalency is the sharing of electrons between the atoms of non-metals. A covalent bond is formed when two atoms of non-metal contribute electron(s) equivalent to their valencyValency or Valence of an element is a measure of an atom's ability to combine with other atoms to create molecules or chemical compounds. More for sharing.
After the bonding, both atoms will attain a stable octet or duplet structure of rare gases. Electrons are not transferred because the atoms involved are electron acceptors. The pair of electrons shared is known as the shared pair of electrons.
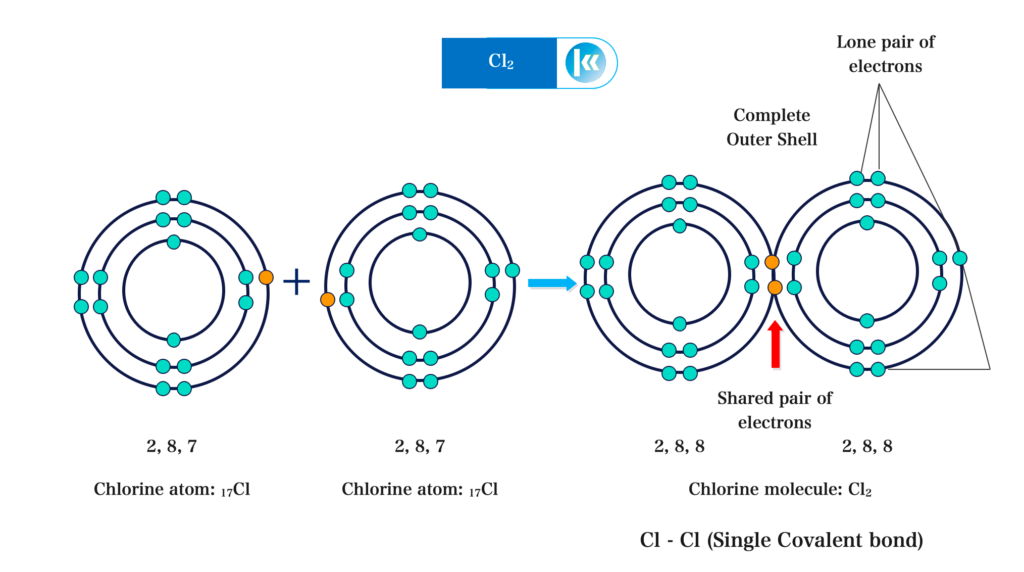
Diatomic molecules are formed by covalent bonding. e.g. Cl2, H2, N2, O2. In Chlorine molecules, only one electron is used in forming a covalent bond. The other six electrons form three lone pairs of electrons.
Formation of Chlorine molecule (Cl2):
Formation of Hydrogen molecule (H2):
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses