Topic Content:
- Meaning of ElectrovalentAn electrovalent or ionic bond is formed when a metal atom transfers one or more electrons to a non-metal atom. Ionic or electrovalent compounds are those compounds which are formed by... More Bonding
- Formation of Sodium Chloride (Na+Cl–)
- Structure of Sodium Chloride
- Formation of Magnesium Oxide (Mg2+O2-)
- Formation of Calcium Fluoride (Ca2+2F–)
- Characteristic Properties of Electrovalent (Ionic) Compounds
The main principle of this type of bonding is donor/acceptor principle.
Electrovalent bonding is the complete transfer of electrons from the outermost shell of a metal to the outer-most shell of a non-metal.
The metals donate electrons while non-metals accept electrons. After combination, both the metal and non-metal will form a stable structure i.e. attain the octet or duplet structure of rare gases.
The metals are positively charged, while the non-metals are negatively charged.
Example:
Formation of Sodium chloride (Na+Cl–):
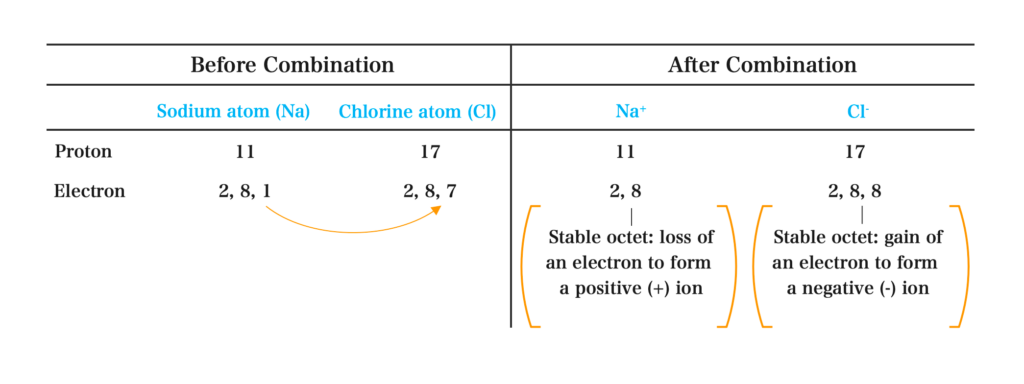
Equation for the Reaction:
\( \scriptsize Na \: \rightarrow \: Na^+ \:- \: e^- \) ………….(i)
\( \scriptsize Cl \: \rightarrow \: Cl^- \: + \: e^- \) ………….(ii)
Add equation (i) and (ii) together
The e– cancel out
\( \scriptsize Na \: + Cl \: \rightarrow \; Na^+ Cl^- \)
Diagrammatic Representation:
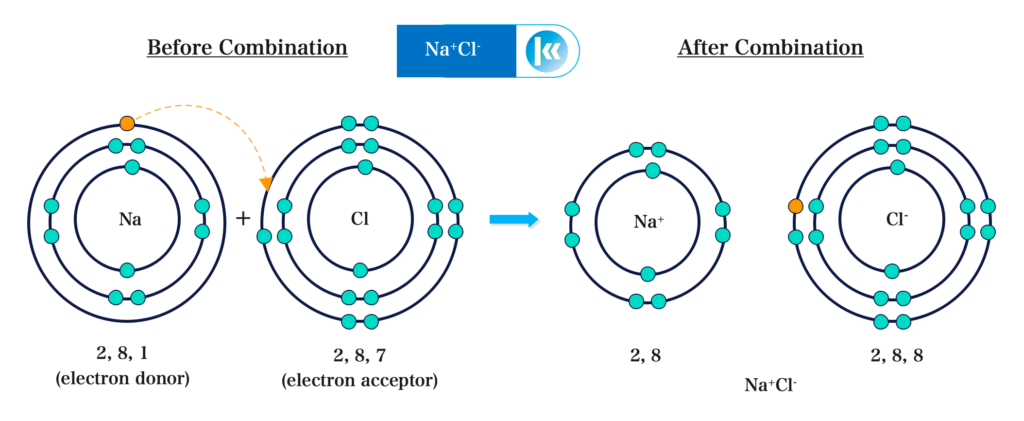
Structure of Sodium Chloride:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses