Topic Content:
- Introduction – Covalent Molecules
- Linear Shape
- Tetrahedral Shape
- Angular Shape
- Trigonal Shape
- Trigonal Pyramidal Shape
- Trigonal Planar Shape
Introduction – Covalent Molecules:
In Covalent Molecules, atoms combine by sharing electrons.
Covalent molecules have a definite shape due to the fact that Covalent bonds are rigid and highly directional. However, the Ionic bondsAn electrovalent or ionic bond is formed when a metal atom transfers one or more electrons to a non-metal atom. Ionic or electrovalent compounds are those compounds which are formed by... More are not directional. Shapes of Covalent molecules are as follows:
1. Linear Shape:
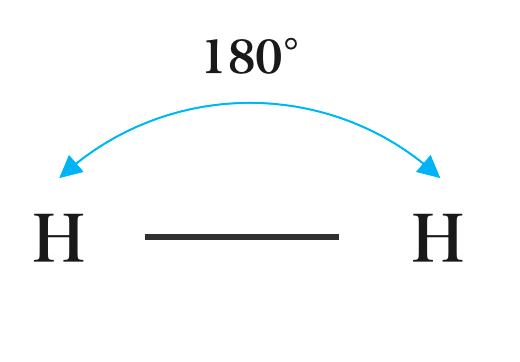
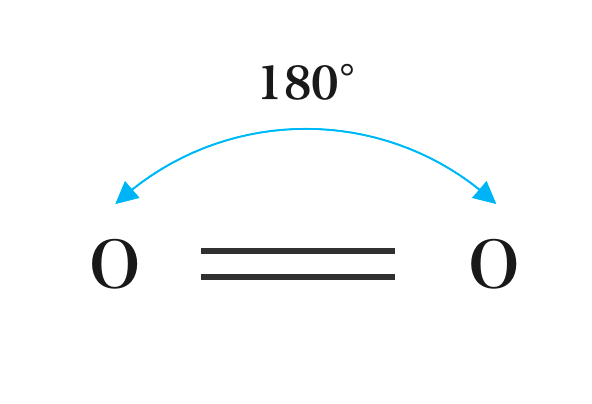
All diatomic molecules are Linear in shape e.g. H2, Cl2, O2, N2. Other Compounds that have a Linear shape are CO, HCl, HF, CO2, SO2, etc. A linear molecule is a molecule in which atoms are deployed in a straight line, and the bond angle is 180°C.
The Linear shape of Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Chloride:
(a) Hydrogen (H2)
(b) Oxygen (O2)
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses