Topic Content:
- Arrangement of Particles in an Atom
- EnergyEnergy is the ability to do work. Energy exists in several forms such as heat, kinetic or mechanical energy, light, potential energy, and electrical energy. Units of Energy: The SI unit... More Levels and Maximum Number of Electrons
- Electronic configuration of the 1st 20 Elements
- Theory Questions
In 1913, a scientist Niels Bohr forwarded his own model of the atom based on the quantum mechanics originally developed by Planck.
He proposed that the model of an atom consists of an extranuclear part known as an electron which is located in spherical orbits (shell) around the nucleus. The orbit/energy level is designated by Letters ( K, L, M, N). These labels correspond to the principal quantum numbers 1, 2, 3, 4… respectively.
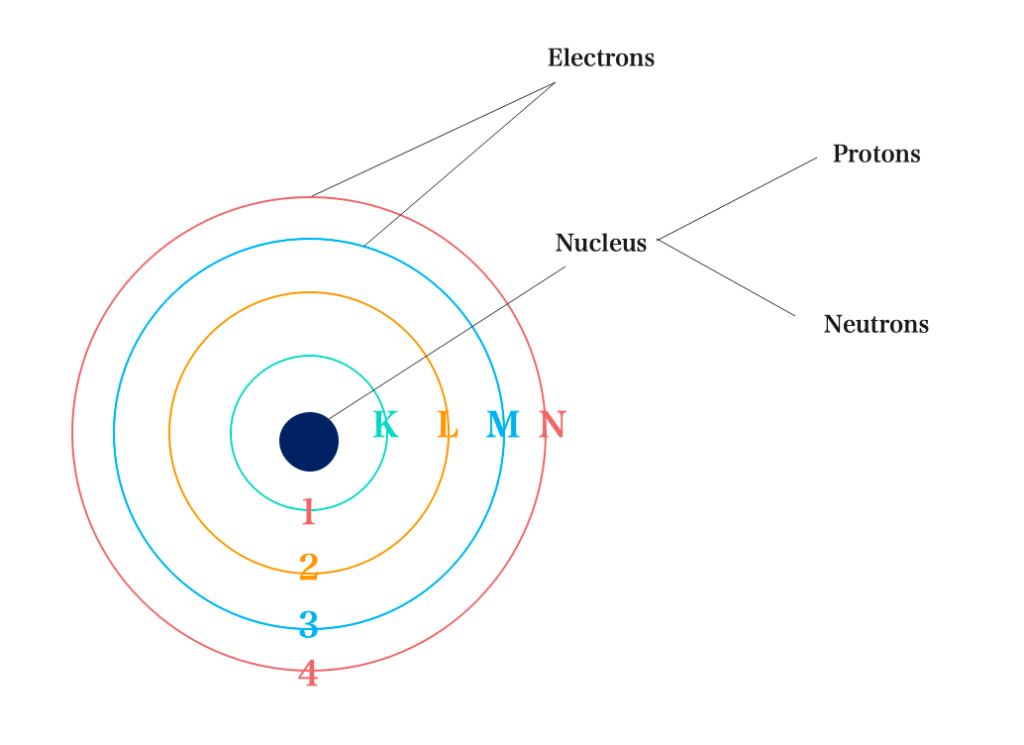
Energy Levels and Maximum Number of Electrons:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!




Responses