Definition of Production:
Production can be defined as the act of providing goods that have utilitythe state of being useful, profitable, or beneficial. More and services that can be paid for. People whose work involves providing goods and services that satisfy human wants are called producers.
Production, which can be defined as the creation of utility or production, is the creation of goods and services to satisfy human wants.
It is also the transformation of raw materials to finished products and their distribution to the final consumer. It includes the creation of tangible goods, e.g. chairs, mobile phones, mirrors, wristwatches, etc. and professionally rendered services like doctors, teachers, cooks, barbers, e.t.c.
Production is set to be complete when the goods, and services produced, reach the final consumers.
Division of Production:
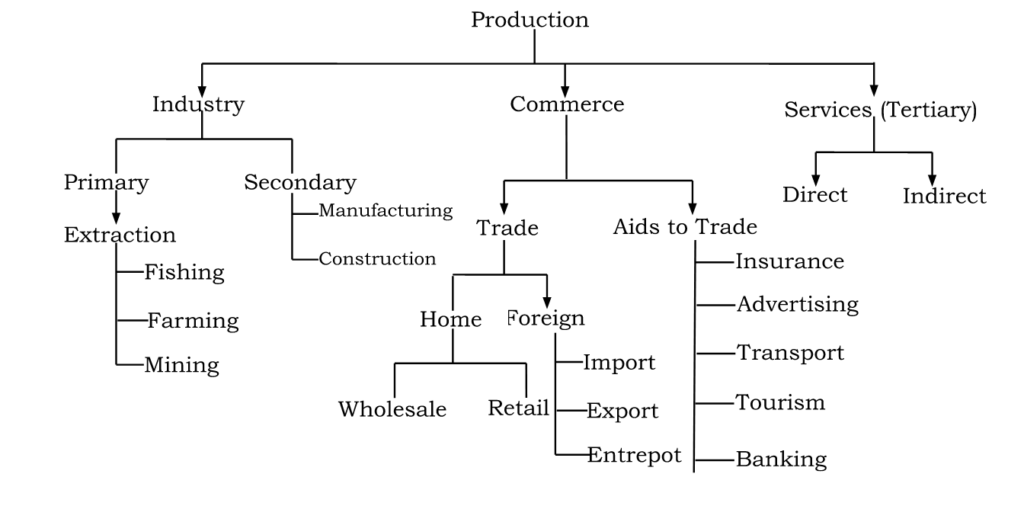
There are two distinguishing features of production which are as follows:-
1. The activity must provide a human need which means somebody must be willing to offer something in exchange for the goods or services.
2. The goods or services must be available for purchase by the final consumers or end-users.



Responses