Definition of Exchange:
This is the idea of giving out one thing in place of another thing, that you receive. Exchange means giving and receiving which takes place among individuals, firms, governments, and countries based on different measures.
To ensure even distribution of goods, services, and wealth in societyThe term society is derived from the Latin word 'socius' meaning friendship or companionship. Society is a community, nation or group of people who share the same traditions, institutions, rules and... More and the world as a whole there must be the practice of exchange. The three forms of exchange are; trade by barter, cash trade, and counter trade.
i. Barter Trade: This involves the exchange of goods for goods and services for services. It is the oldest type of exchange that existed in primitive society.
ii. Cash Trade: This came into existence as a result of the introduction of money which is generally accepted as a medium of exchange of goods and services between firms, individuals or countries.
iii. Counter trade: This involves the exchange of goods and services between firms or countries in which goods and services serve as a measure of value without the use of money. It is regarded as the advanced and modern form of barter trade.
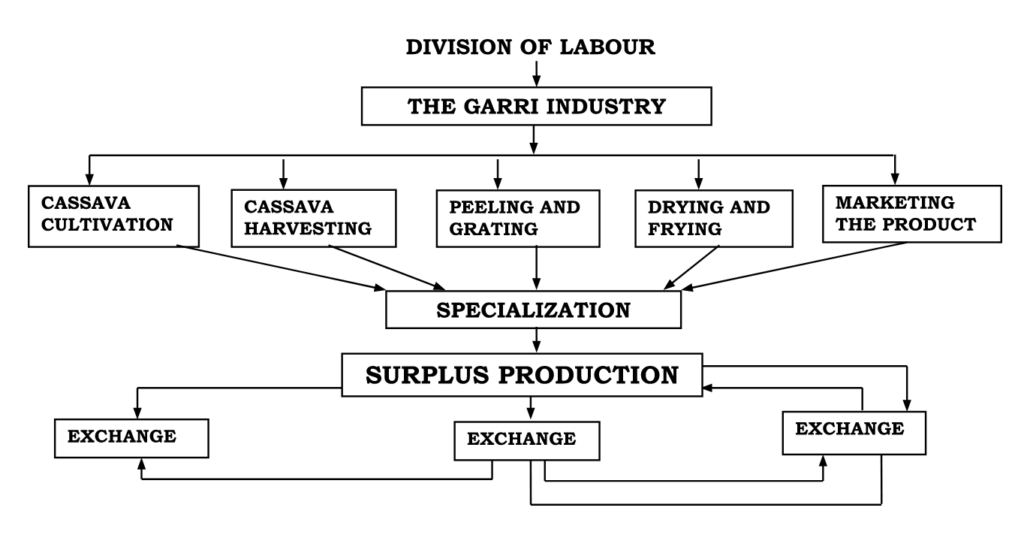
Often, exchange is regarded as an outcome of production and specialization. Surplus production can be enhanced by division of labour and specialization. To obtain what others produce, an exchange must be made. Therefore specialization facilitates production and trade.



Responses