Topic Content:
- Measurement of Volume
- For a regular object
- For an irregular object
- For a cone
- For a cylinder
Objects that have definite shapes are called regular objects. Objects that do not have definite or regular shapes are called irregular objects.
Regular objects have all their sides and lengths equal. Irregular objects do not have their sides and lengths equal. Regular objects include objects like cubes and cuboids. Examples of irregular objects include a piece of stone, pieces of broken glass, a piece of paper, a piece of brick, a leaf, etc.
For a Regular Object:
For a regular object, the volume can easily be calculated by measuring length (l), breadth (or width) (b), and height (h).
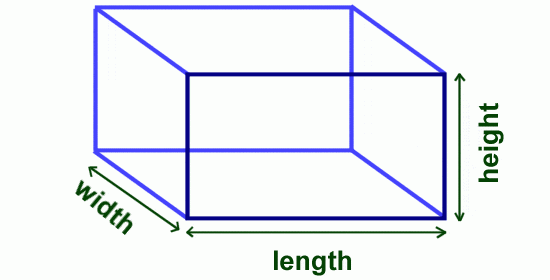
Volume = length × breadth × height = l × b × h
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



The pictures make it easy to understand.