Topic Content:
- Potential Difference
We will be discussing electric circuits in more detail in third term.
An electric circuit is the path through which electric current flows in a circuit. It consist of the source of electric energyEnergy is the ability to do work. Energy exists in several forms such as heat, kinetic or mechanical energy, light, potential energy, and electrical energy. Units of Energy: The SI unit... More (e.g. a battery) connected through a conductor (e.g. a wire) to a load (e.g. a light bulb) and a switch. The purpose of a switch in a series circuit is to make it easy to open or close the electrical circuit, turning the flow of electricity on or off.
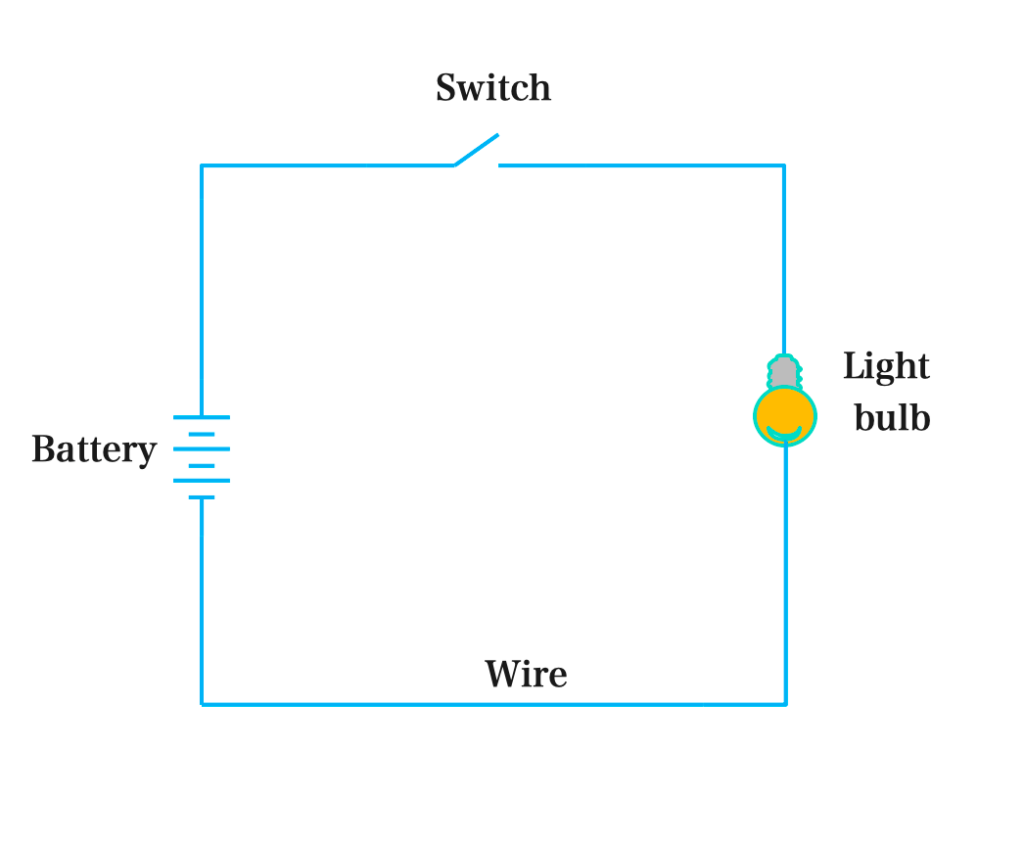
In electric circuits, current is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. A wire is a single conductor, typically made of copper, aluminum, or sometimes steel (non – electrical use).
When a current is allowed to flow between two points, a difference in potential is said to occur between the points and this is referred to as potential difference or voltage.
Potential Difference:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses