Topic Content:
- Meaning of Conduction
- Experiment to show that Water is a Poor Conductor of Heat
- Experiment to Compare Thermal Conductivity of Different Materials (Ingen Hauz’s Experiment)
- Using Kinetic Molecular Theory to Explain Conduction in Solids
- Application of Conductors & Insulators
It is a common experience that when hot water is poured into a stainless cup, the cup becomes hot after a few minutes as a result of heat transfer from the hot water to the stainless cup; this process of heat transfer is called conduction.
Conduction is a process of heat transfer through a material, with the average position of the particle material remaining the same.
It depends on the difference in temperature of the hot and cold body for conduction to take place. The materials involved must allow heat energyEnergy is the ability to do work. Energy exists in several forms such as heat, kinetic or mechanical energy, light, potential energy, and electrical energy. Units of Energy: The SI unit... More to pass through them and such materials are called conductors.
A conductor is a substance that allows heat energy to flow through it e.g. most metals are good conductors of heat.
An insulator is a substance that does not allow heat energy to flow through it e.g. wood, plastic, rubber, and wool.
Experiment to show that Water is a Poor Conductor of Heat:
Set up:
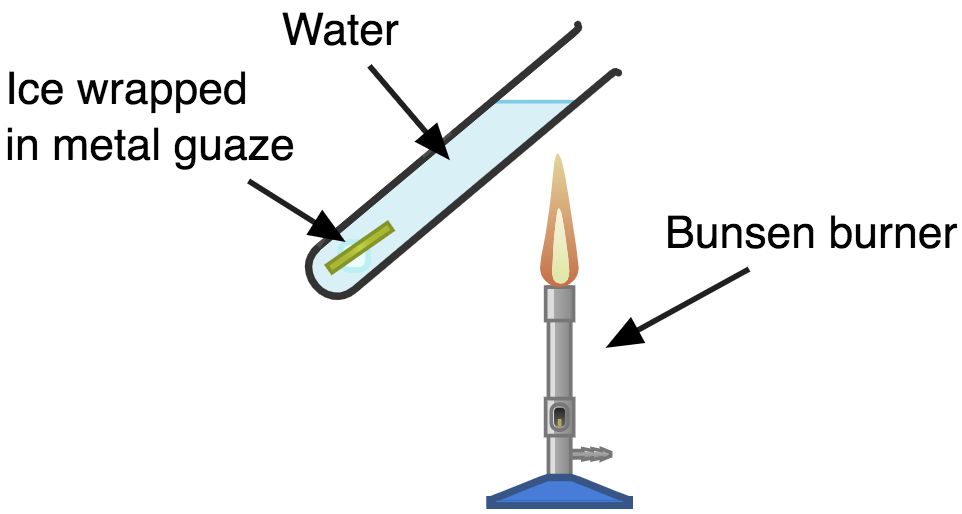
Aim:
To demonstrate that water is a poor conductor
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses