Topic Content:
- The Mammalian Digestive System
The alimentary system is an organ system within humans and other animals concerned with the ingestionIngestion is the process of taking food into the body through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. More, digestionDigestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed... More and absorptionAbsorption is the movement of digested food molecules from the digestive system into the blood (glucose and amino acids) and lymph (fatty acids and glycerol). The small intestine absorbs most of... More of food as well as the removal of waste products (faeces).
The Mammalian Digestive System:
This system is made up of the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs. The gastrointestinal tract, also called the digestive tract or alimentary canal, consists of the mouth or buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The accessory organs are the teeth, tongue, and glandular organs such as salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
All the parts of the system continuously work together to convert the raw materials of food into the nutrients, glucose, fructose, galactose, amino acids, carboxylic acids and glycerol, that keep the body alive. Solid wastes are expelled.
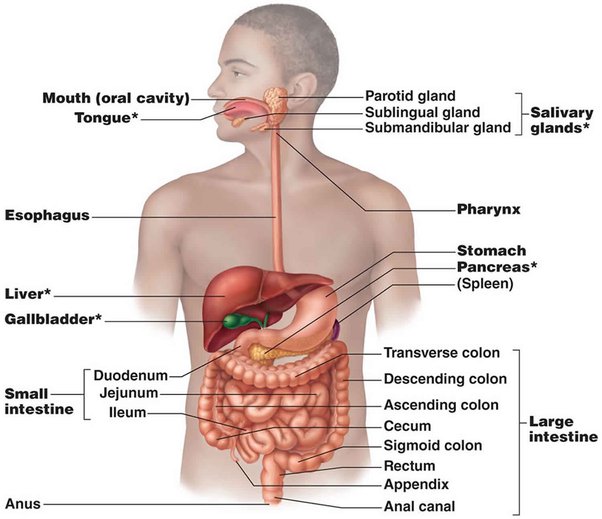
The organs that make up the human digestive system include;
Mouth and Buccal Cavity:
Ingestion is the taking in of solid food by the organism through the mouth.
The mouth contains the teeth, salivary gland and tongue. In the mouth, food is masticated or broken down into small pieces by the teeth, and salivary glands present in the mouth secrete saliva to soften the food. The saliva contains an enzyme called ptyalin which converts cooked starch to complex sugars (maltose). The tongue mixes the food with saliva after which it is rolled into a ball or bolus, which is then swallowed.
Pharynx:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses