Topic Content:
- Electrolysis of Dilute Tetraoxosulphate(IV) Acid (Acidified Water)
- Electrolysis of Copper(II) Tetraoxosulphate(VI) Solution Using Different Anodes
- Electrolysis of a Gaseous Copper(II) Tetraoxosulphate(IV) Solution Using Copper Electrodes
- Electrolysis of Concentrated CuCl2
Electrolysis of Dilute Tetraoxosulphate(IV) Acid (Acidified Water):
Water containing a small amount of acid dissolved in is called acidified water.
In the electrolysis of acidified water, dilute sulphuric acid is preferred over other mineral acids like dilute nitric or hydrochloric acid, for acidification of water. Since water is a non-electrolyte, the addition of sulphuric acid makes it a conductor of electricity.
Dilute sulphuric acid is preferred because the nitrate ions or chloride ions in dilute nitric and dilute hydrochloric acid respectively may interfere with the reactions.
The electrolytic cell used for acidified water is known as the Hofman voltameter. The electrodes used are platinum foil.
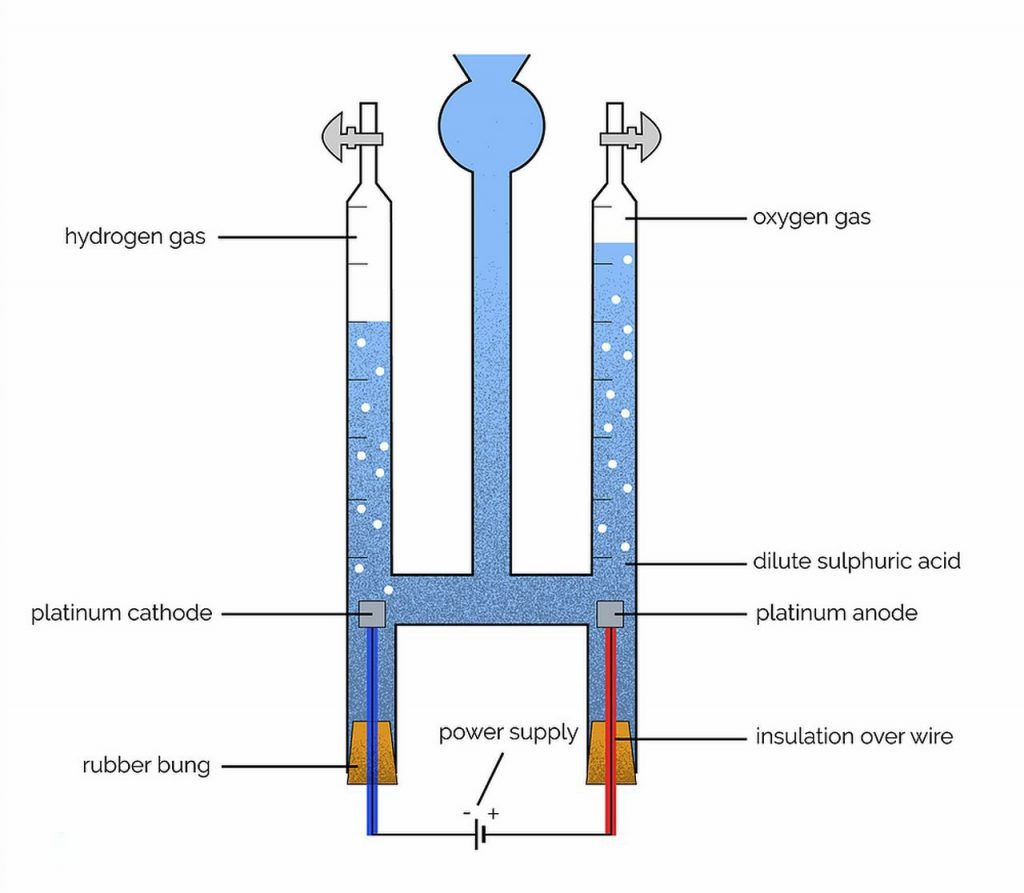
The ions present in the electrodes are:
H2SO4(aq) ⇌ 2H+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
H2O(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + OH–(aq)
At the cathodeA cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves the electrolyte. It is the negative part of the cell where reduction takes place. More:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses