Back to Course
SS2: CHEMISTRY - 1ST TERM
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Periodicity and Periodic Table I | Week 15 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Quantum Numbers Orbitals & Electrical Structure | Week 26 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Periodicity and Periodic Table II | Week 312 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Periodic Table and Atomic Properties
-
Melting and Boiling Point
-
Electrical and Thermal Conductivities
-
Atomic Size [Radius]
-
Ionic Size [Radius]
-
Atomic Volume
-
Ionization Energy
-
Electron Affinity
-
Electronegativity
-
Differences between Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity
-
Summary of Trends of Atomic Properties
-
Theory Questions - Periodicity and Periodic Table II
-
Periodic Table and Atomic Properties
-
Periodicity and Periodic Properties III | Week 411 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Periodicity and Periodic Properties IV | Week 55 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Mass-Volume Relationship in Reaction | Week 68 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Types of Reactions: Oxidation and Reduction | Week 7 & 87 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Oxidation – Reduction Reaction II | Week 93 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Electrode Potential and Electrochemical Cells I | Week 106 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Electrode Potential and Electrochemical Cells II | Week 115 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Electrolysis I | Week 128 Topics|1 Quiz
-
Electrolysis II | Week 138 Topics|1 Quiz
Lesson 1,
Topic 3
In Progress
Metals and Non-Metals
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
Topic Content:
- Metals and Non-Metals
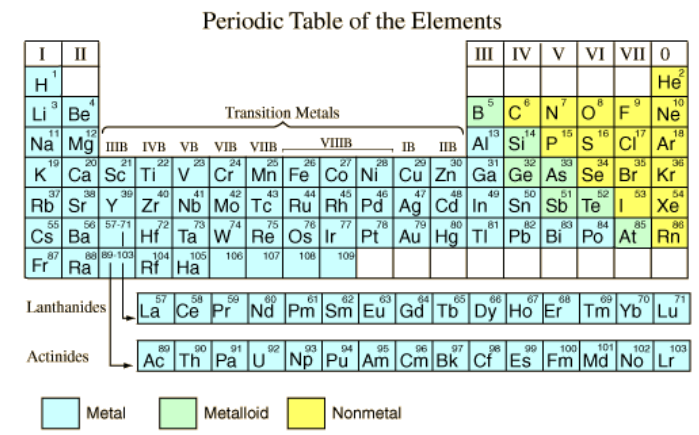
In the periodic table, elements are classified into metals and non-metals.
Groups I – III are metals, they donate their valence electrons.
Groups IV – VIII are non-metals that accept or share electrons.
Group 0 are the noble gases, their outer electrons are filled up.
Semi-metals or metalloids occur along the boundary line. For example, carbon is a non-metal, silicon and germanium are metalloids, while tin and lead are metals.



Responses