Topic Content:
- Definition of Couple
- Applications of Torque
A couple is a system of two equal and parallel but opposite forces not acting in a straight line. This system of forces in parallel can cause a body to rotate and not move in a straight line (linearly).
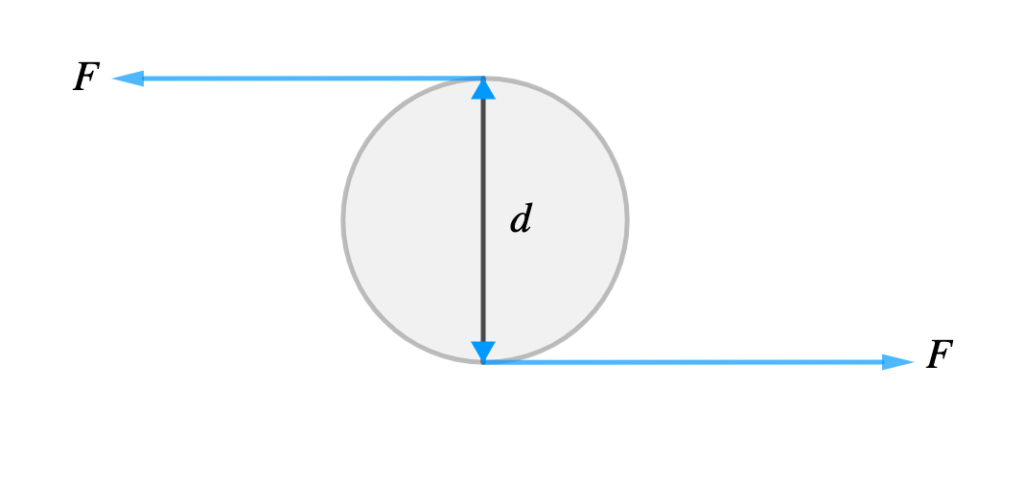
The moment of a couple is the product of one of the forces and the perpendicular distance between the lines of action of the two forces.
From Fig. 1 above;
Moment of a couple = Force × perpendicular distance
Moment = F × d
Moment = F × 2r
where r is the radius of the wheel and d is its diameter.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



The teachings are beneficial