
Considering right angle triangle LMO
Cos θ = \( \frac {r}{R} \)
i.e. r = R Cos θ
Example 1:
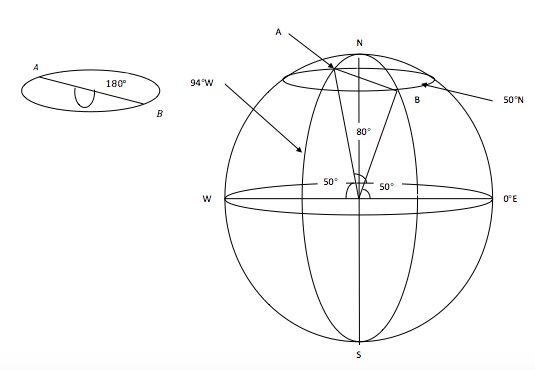
Find the distance between two points A(50oN, 94oW) and B(50oN, 86oE):
(i) Along the parallel of Latitude
(ii) Along a great circle
Solution:
(i) Angular difference = 94o + 86o = 180o
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} = \normalsize \frac{180}{360}\scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; cos50\)
= \( \frac{1}{2} \; \times \; \frac{44}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; 0.6428\)
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} = 12,929.213 \)
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} = 13,000km \;(nearest\;kilometre) \)
(ii) Angular difference = 180o – (50 + 50)o
= 180o – 100o
= 80o
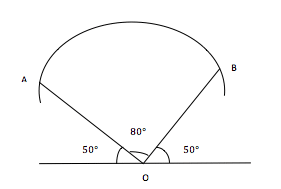
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} = \normalsize \frac{80}{360}\scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \)
= 8,939.6
i.e. \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} \) = 8,940Km (nearest Kilometre).
(Recall that it is clear that distance along a great circle is shorter i.e. 8,940Km < 13,000Km.
Example 2
Two points A and B are 800Km apart on the same Latitude with 20o angular difference of longitude. Calculate:
(i) The Latitude
(ii) The speed of an aeroplane that travelled from A to B in 2hours
(iii) The speed of the point B due to the rotation of the earth. (Take \(\scriptsize \pi = \normalsize \frac{22}{7}\) and R = 6,400Km.)

Solution:
\( \scriptsize \bar{AB} = \normalsize \frac{20}{360} \scriptsize\; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; cos θ\) \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} = \normalsize \frac{1}{18}\scriptsize \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{44}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; cos θ\) \( \scriptsize 800 = \normalsize \frac{1}{18} \scriptsize \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{44}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; cos θ\)cos θ = \( \frac{18 \; \times \; 800 \; \times \; 7}{44 \; \times \; 6400} \)
θ = cos-1(0.3580)
θ = 69°
Let θ Latitude = θ° N
∴ θ = 69° N
(ii) Speed = \( \frac{Distance}{time} \)
Time = 2hours, Distance = 800
i.e. Speed(s) = \( \frac{800}{2} \)
Therefore, Speed = 400Km/h
(iii) Circumference of Latitude 69o = 2 πr
Where r= RCos θ
i.e. Distance = \( \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; cos 69\)
= 14,417Km
Therefore, Speed = \( \frac{Distance}{time} = \frac{14,417}{2} \)
= 7,208 Km/h.
Example 3
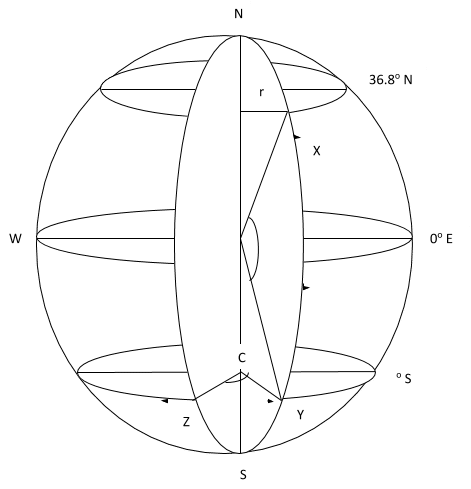
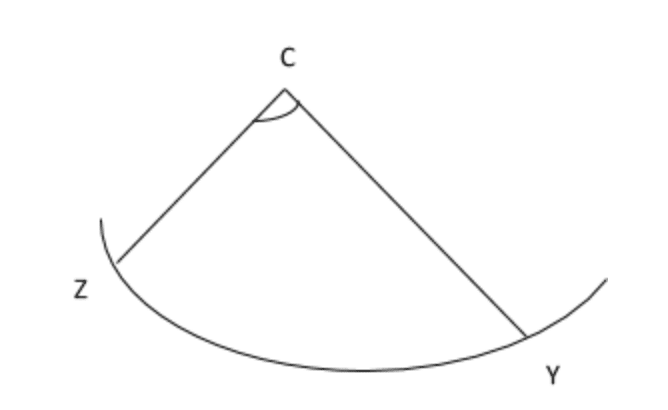
A plane leaves an airport X, 20.6oE and 36.8oN and flies due South along the same longitude for 8hours at the rate of 1000Km/h to another airport Y, 20.6oE, and θ°. The plane then flies west to another airport Z for 8hours at the same speed.
Calculate, to the nearest degree:
(i) The value of
(ii) The longitude of Z
(Take π = \( \frac{22}{7} \) and R = 6,400Km.)
(i) Distance \( \scriptsize \bar{XY}\) = Speed x time
= 1000 x 8
= 8,000Km
i.e. \( \scriptsize \bar{XY} = 8000 = \frac{θ}{360} \scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \)
i.e. 8000 = θ × 117.46032
i.e. θ = 71.5909
θ = 72° nearest degree.
Angular difference = θ° S + 36.8°N
72 = θ + 36.8
θ = 35.2°
θ = 35°S nearest degrees.
(ii) \( \scriptsize \bar{ZY}\) = Speed x time
\( \scriptsize \bar{ZY}\) = 1000 x 8
i.e. \( \scriptsize \bar{ZY}\) = 8,000Km
i.e. \( \scriptsize \bar{ZY} = 8000 = \frac{θ}{360} \scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; cos 35.2 \)
i.e. 8000 = θ × 91.312699
i.e. θ = 87.6110335
i.e. Angular difference = 20.6oE + θ°W
i.e. 87.611 = 20.6 + θ°W
i.e. θ°W = 67.011°W
Example 4:
A and B are two points on latitude 55oS and their longitudes 23oW and 33oE respectively. Calculate the distance between A and B along:
(i) A great circle
(ii) The parallel of Latitude
(Take π = \( \frac{22}{7} \) and R = 6,400Km.)
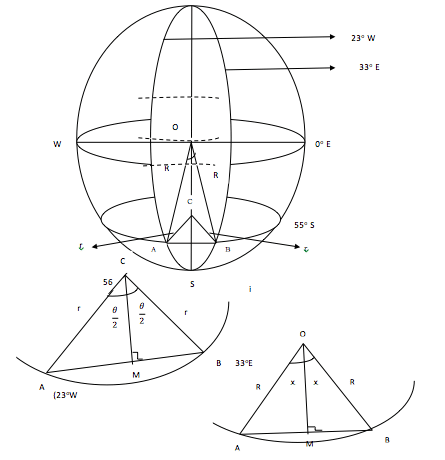
:- \( \scriptsize \bar{AM} = r sin \normalsize \frac {θ}{2}\)
\(\scriptsize \bar{AM} = Rcos(Latitude) sin \normalsize \frac{\theta}{2} \) ………….….(a)
\( \scriptsize \bar{AM} = R \)i.e. \( \scriptsize \bar{AM} = R sin x\) ………………… (b)
Equate equation (a) and (b)
R cos (latitude) \( \scriptsize sin \normalsize \frac {θ}{2}\scriptsize = R sin x \)
Therefore \( \scriptsize sin x = cos \; (latitude) \; sin \normalsize \frac {θ}{2} \)
i.e. sin x = Cos 55 Sin 28
i.e. x = sin -1 (0.5736×0.4695)
= sin -1 (0.2693 )
x = 15.6219
2x = 31.24° =31°
Therefore, \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} \) along a great circle = \( \frac{2x}{360} \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \pi r \)
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{AB}= \normalsize \frac{31.24}{360}\scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \)
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} \) = 3,491.38
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} \) = 3,491 km
(b) \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} \) along parallel of Latitude = \( \frac{θ}{360}\scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \pi R cos \; (latitude) \)
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} =\normalsize \frac{56}{360}\scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; cos 55 \)
= 3,589.31
i.e. \( \scriptsize \bar{AB} \) = 3,589Km.
Example 5
The position of P is (60oS, 60oW) and that of Q is (60oS, 32oE). Calculate the distance between P and Q along:
(i) The parallel of Latitude
(ii) A great circle
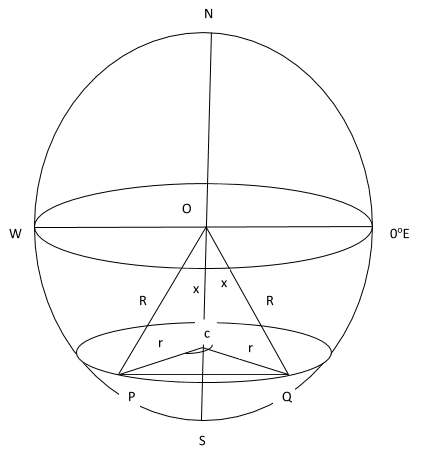
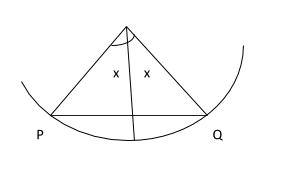
(i) \( \scriptsize \bar{PQ} = \normalsize \frac{θ}{360}\scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \pi R cos \; (latitude) \)
i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{PQ} = \normalsize \frac{θ}{360} \scriptsize \; \times \; 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \; \times \; cos 60 \)
\( \scriptsize \bar{PQ} \) = 5,140.3174603
\( \scriptsize \bar{PQ} \) = 5,140Km
(ii)Sin x = Cos 60 Sin46
= 0.5000 x 0.7193
Sin x = 0.3600
x = Sin-1(0.3600)
x = 21.1o
2x = 42.2o
2x = 42o
\( \scriptsize \bar{PQ} = \normalsize \frac{2x}{360}\scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \pi R \)i.e \( \scriptsize \bar{PQ}= \normalsize \frac{42}{360}\scriptsize \; \times \; \scriptsize 2 \; \times \; \normalsize \frac{22}{7} \scriptsize \; \times \; 6400 \)
= 4,693.333
PQ = 4,693Km.



Responses