An alternating current (A.C) is the one that varies sinusoidal in such a way as to reverse its direction periodically.
An a.c is represented by
I = IOsinωt = IOsin2πft
I = instantaneous current
f= frequency
ωt= phase angle of the current
ω = angular velocity
IO= maximum or peak current
Also, alternating voltage is
V= VOsinωt = VOsin2πft
Peak and r.m.s Values of A.C
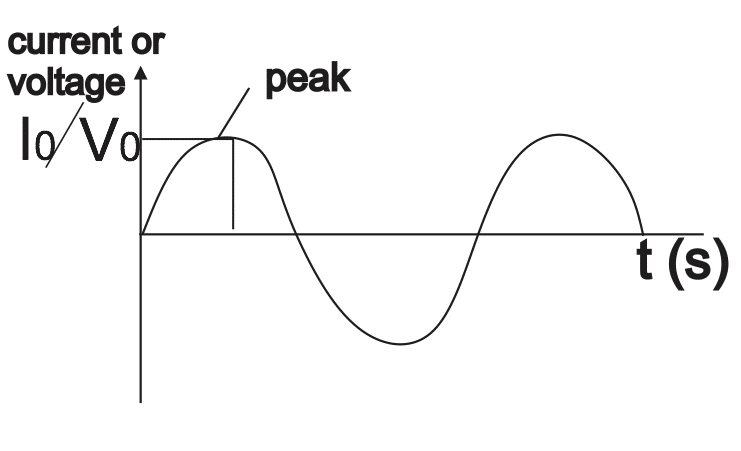
The peak value of an a.c current is the maximum value or the amplitude of the a.c current or voltage.
The average value of an a.c current is the sum of the current /voltage above the zero line. The average is zero as it changes between maximum position and negative maximum.
Root mean square (r.m.s) current is that steady current that will develop the same quantity of heat in the same time in the same resistance.
The r.m.s value for the current is
Ir.m.s = \( \frac {I_0}{\sqrt{2}} \)
Ir.m.s = 0.707I0
Vr.m.s = 0.707V0.
Example
An a.c current has a peak value of 4A, calculate: (i) r.m.s current (ii) current at an instant when ωt = 600 and 1500
Solution
(i) Ir.m.s = 0.707I0
= 0.707 x 4
= 2.83A
(ii) I = I0Sinωt
= 4Sin60 = 3.46A
- I = I0Sinωt
= 4Sin150 = 2A



Good
Very good