WAEC: COMMERCE
Quizzes
-
2014 Commerce WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2014 Commerce WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2015 Commerce WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2015 Commerce WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2016 Commerce WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2016 Commerce WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2017 Commerce WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2017 Commerce WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2018 Commerce WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2018 Commerce WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2019 Commerce WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2019 Commerce WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2020 Commerce WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2020 Commerce WAEC Theory Past Questions
-
2021 Commerce WAEC Objective Past Questions
-
2021 Commerce WAEC Theory Past Questions
Quiz Summary
0 of 8 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 8 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 8
1. Question
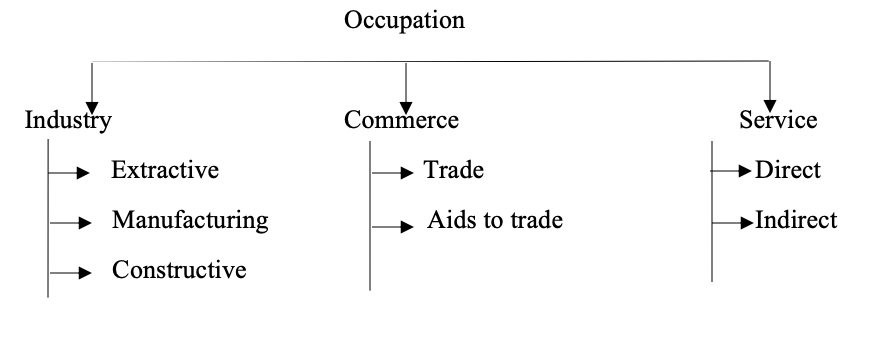
(a) What is occupation?
(b) With the aid of a diagram, show the different classes of occupation.
(c) Explain with one example each, three classes of occupation shown in 1 (b) above.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 2 of 8
2. Question
(a) What is a vending machine?
(b) State six reasons why supermarkets are popular with shoppers.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 3 of 8
3. Question
(a) Outline five functions of commercial banks.
(b) List and explain five ways the central bank controls the commercial banks.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 4 of 8
4. Question
(a) State five reasons for the presence of the customs and excise authority at seaports.
(b) Explain five functions of airport authority
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 5 of 8
5. Question
(a) Explain five reasons for which manufacturers advertise their products.
(b) State five reasons for the continued criticism of advertising.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 6 of 8
6. Question
(a) What is a contract?
(b) List and explain four ways by which a contract can be discharged.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 7 of 8
7. Question
(a) State five reasons for governments participation in business
(b) Explain five problems encountered by government businesses.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -
-
Question 8 of 8
8. Question
(a) Write in full the following abbreviations as used in commerce:
(i) COD (ii) CIF (iii) FOB; (iv) E and O.E.
(b) The sale of consumer goods costing N 100,000 attracts a cash discount of 7.5% and a quantity discount of 5%. Calculate the:
(i) Value of the quantity discount
(ii) Value of the cash discount
(iii) The net amount of money payable by the buyer.
-
This response will be reviewed and graded after submission.
Grading can be reviewed and adjusted.Grading can be reviewed and adjusted. -



Responses