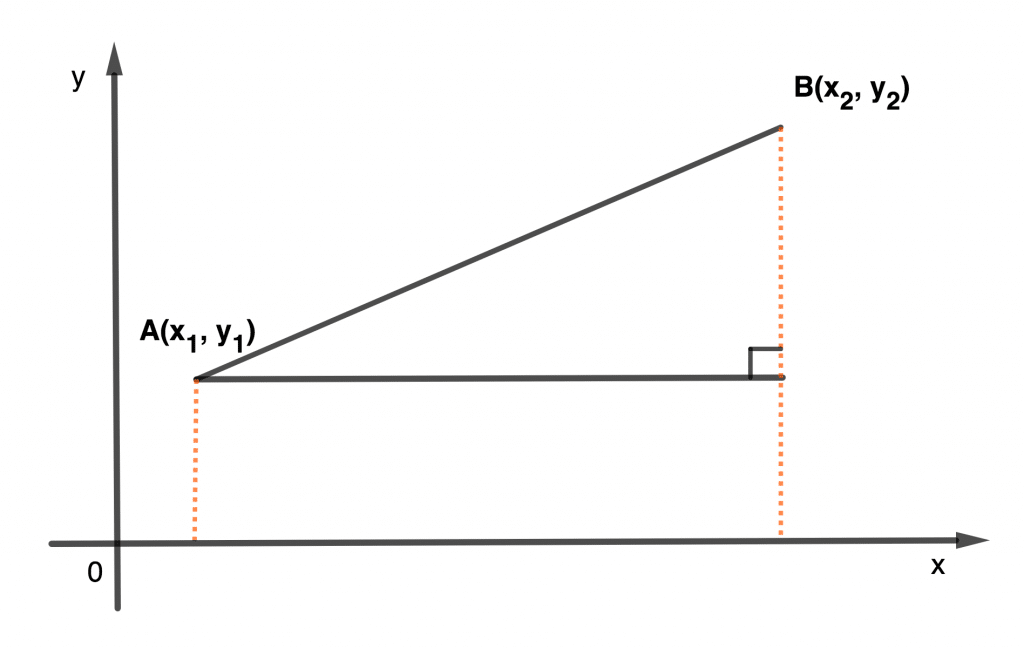
If A, B have coordinates (x1, y1), (x2, y2) respectively as shown in the diagram below, then by Pythagoras theorem:
|AB|2 = (x2 – x1)2 + (y2 – y1)2
AB = \( \scriptsize \sqrt {\left ( x_2 \; – \; x_1 \right)^2 \;+\; \left ( y_2 \; – \; y_1 \right )^2} \)
Example:
Find the distance between the points
i. A(2, 5) and B(5, 9)
ii. A(3, -6) and B(2, 0)
Solution
i.
x1 = 2, y1 = 5
x2 = 5, y2 = 9
AB = \( \scriptsize \sqrt {\left ( x_2 \; – \; x_1 \right)^2 \;+\; \left ( y_2 \; – \; y_1 \right )^2} \)
Substitute in the values of x and y into the equation
AB = \( \scriptsize \sqrt {\left ( 5 \; – \; 2 \right)^2 \;+\; \left ( 9 \; – \; 5 \right)^2} \\ = \scriptsize \sqrt { (3)^2 \;+\; (4)^2 }\\ =\scriptsize \sqrt { 9 \;+\; 16} \\ = \scriptsize \sqrt { 25} \\ =\scriptsize 5\)
ii.
x1 = 3, y1 = -6
x2 = 2, y2 = 0
AB = \( \scriptsize \sqrt {\left ( x_2 \; – \; x_1 \right)^2 \;+\; \left ( y_2 \; – \; y_1 \right )^2} \)
Substitute in the values of x and y into the equation
AB = \( \scriptsize \sqrt {\left ( 2 \; – \; 3 \right)^2 \;+\; \left ( 0 \; – \; ( \; – 6)^2 \right)} \\ = \scriptsize \sqrt { (-1)^2 \;+\; (6)^2 }\\ =\scriptsize \sqrt { 1 \;+\; 36} \\ = \scriptsize \sqrt { 37} \)



Responses