Topic Content:
- Castes of honey bees
- drones, queens, and workers
- roles and functions
- drones, queens, and workers
- Economic importance of Honey Bees
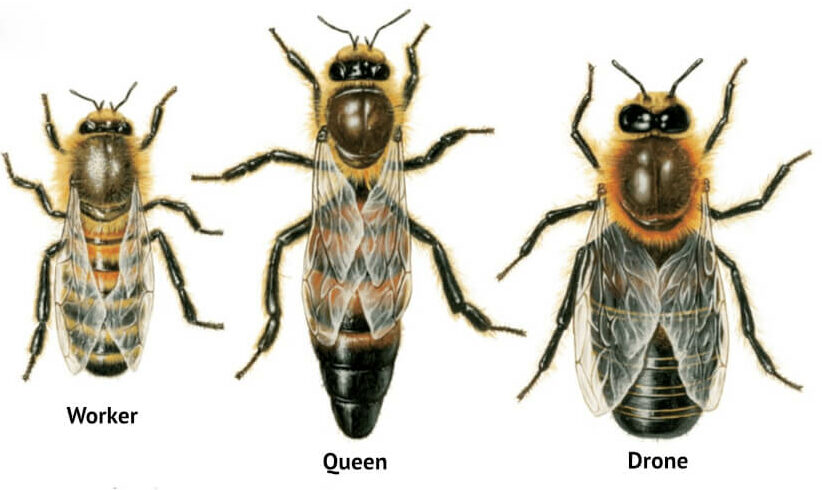
Castes of Honey Bees:
A colony of bees consists of three castes of bees. These are:
A Queen Bee:
This is the only breeding female in the colony. The queen is the only sexually mature female in the hive and all the female worker bees and male drones are her offspring. The queen may live for up to three years or more and may be capable of laying half a million eggs or more in her lifetime. The queen is raised from a normal worker egg but is fed a larger amount of royal jelly than a normal worker bee, resulting in radically different growth and metamorphosis. The queen influences the colony by the production and dissemination of a variety of “pheromones” or “queen substance”. One of the chemicals suppresses the development of ovaries in all the female worker bees in the hive and prevents them from laying eggs.
The Worker Bee:
Worker bees are the most numerous members of the colony. A healthy colony may contain 80,000 worker bees or more at its peak growth in early summer. Workers build and maintain the nest and care for the brood.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses