Topic Content:
- Respiratory Organs of Amphibians
- Gills
- Buccal Respiration
- Cutaneous Respiration
Respiratory Organs of Amphibians:
Amphibians are cold-blooded blooded so they do not use up any energyEnergy is the ability to do work. Energy exists in several forms such as heat, kinetic or mechanical energy, light, potential energy, and electrical energy. Units of Energy: The SI unit... More for keeping their bodies at a constant temperature. This means their cells are not working as hard as warm-blooded animals like mammals, and they do not need as much oxygen.
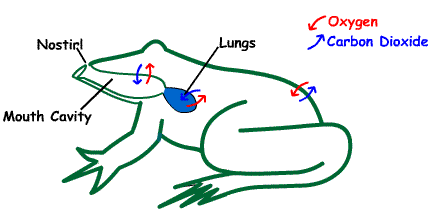
The respiratory organs in amphibians are the gills, lungs, mouth (buccopharyngeal membrane) and the skin (cutaneous breathing).
Gills:
The gills are only specific for the tadpoles and a few other amphibians, which possess gills that help them breathe underwater.
Tadpole uses internal and external gills in order to respire within their aquatic environment. The gills filter oxygen from the water and dispose of respiratory waste products. The gills are lost as the tadpole transitions into a frog.
Buccal Respiration:
The inner lining of the mouth is the buccopharyngeal membrane which allows the exchange of gases with the atmosphere.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses