Topic Content:
- Co-ordinate Covalent or Dative Bonding
- Formation of Ammonium ion (NH4+)
- Formation of Hydroxonium Ion or Oxonium Ion (H2O+)
- The Reaction between Ammonia and Boron Trifluoride, BF3
- Examples of Compounds that Exhibit Co-ordinate Covalent Bond
- Properties of Co-ordinate Covalent Compounds
In co-ordinate covalent bonding, electrons are still shared but it is only one of the participating atoms that donate the pair of electrons to be shared. Such a pair of electrons is called the Lone pair.
Co-ordinate covalent bonding occurs between an atom that has a Lone-pair (unshared pair) of electrons in the outer shell and another atom that has an empty valence orbital and requires one pair of electrons to complete an octet or duplet structure.
The atom that contributes the pair of electrons to be shared is known as donor-atom, while the other is the acceptor atom.
Examples:
Formation of Ammonium ion (NH4+):
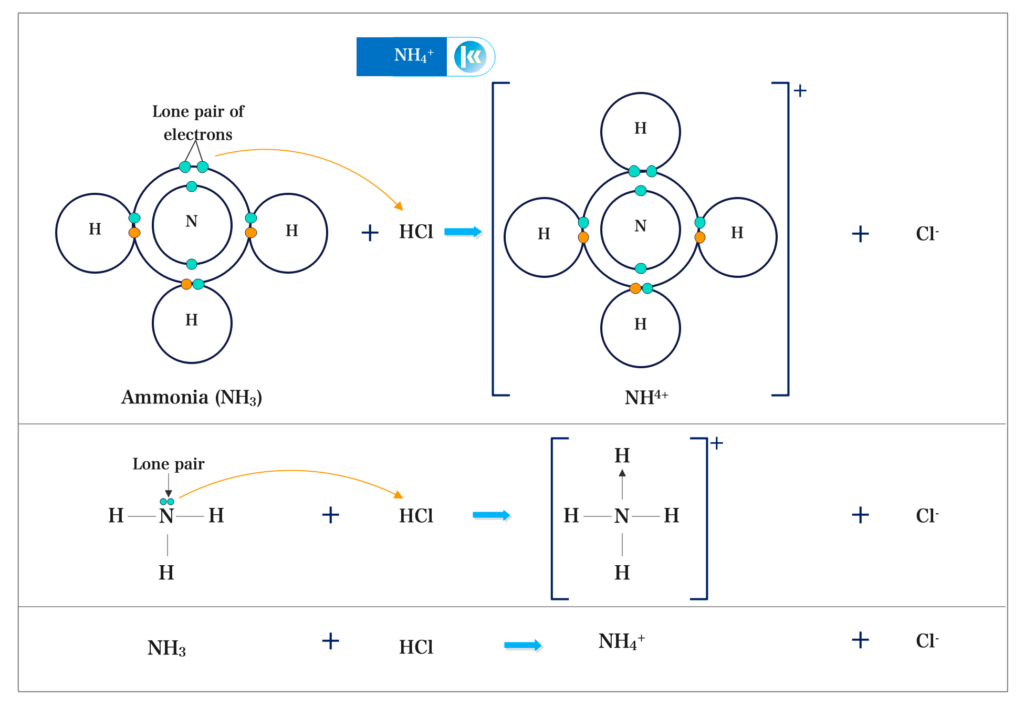
Ammonia and water molecule possess Lone pair and they can enter into a co-ordinate covalent bonding. When Ammonia (NH3) reacts with Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) the H+ from HCl accepts a Lone pair of electrons from Ammonia (NH3) to form a co-ordinate covalent bond.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!





Responses