Topic Content:
- Definition of Aids to Trade
- Examples of Aids to Trade
What are Aids to Trade?
Aids to Trade are those services that facilitate, the buying and selling of goods and services.
Examples of Aids to Trade:
The aids to trade are banking, advertising, insurance, transport, communication, e-commerce, warehousing, and tourism.
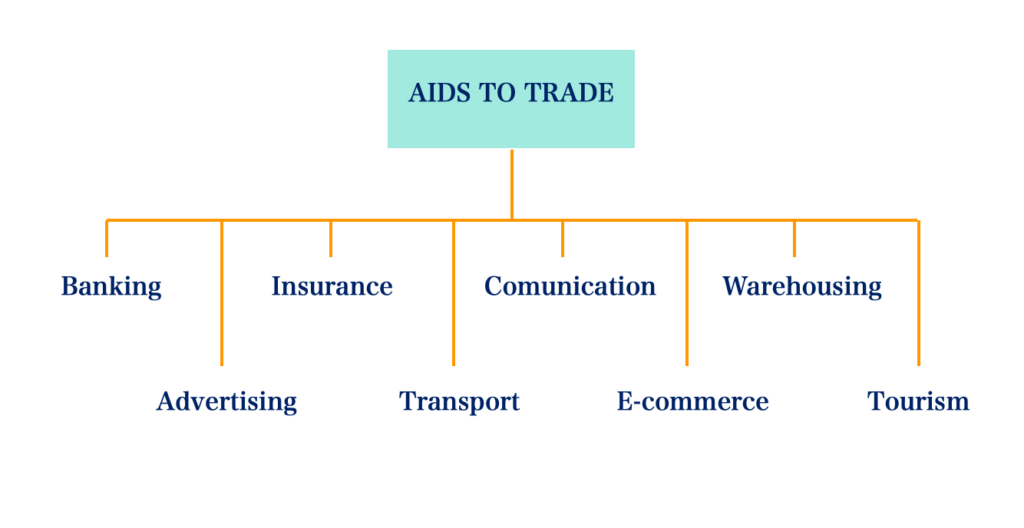
1. Banking:
Banking services are provided by institutions, set up to aid business transactions.
Their services include:
a. Providing businesses with capital, to carry out buying and selling.
b. Helping businesses transfer money, locally or internationally.
c. Helping traders keep their money in the bank.
d. Providing loans for customers to run their businesses.
2. Advertising:
It involves the creation of awareness of existing and new products available for sale, through radio, television, billboards, magazines, and the internet. This helps to increase the sales of goods and services.
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



how does tourism aids to trade
Tourism is a major source of foreign exchange and investment. Aids to Trade are those services that facilitate, the buying and selling of goods and services. It aids trade because it generates employment and provides business opportunities (buying and selling of goods and services).