Topic Content:
- The Cartesian Plane
A Cartesian plane contains two lines, one horizontal i.e. (left to right) and the other vertical (top to bottom) intersecting at a point called the origin (0).
The horizontal line is called the x-axis (abscissa) and the vertical line is called the y-axis (ordinate).
e.g. \( \scriptsize \left( \underset{x\:coordinate}{2} \; \;\: \underset{comma}{,} \;\;\: \underset{y-coordinate}{5} \right) \)
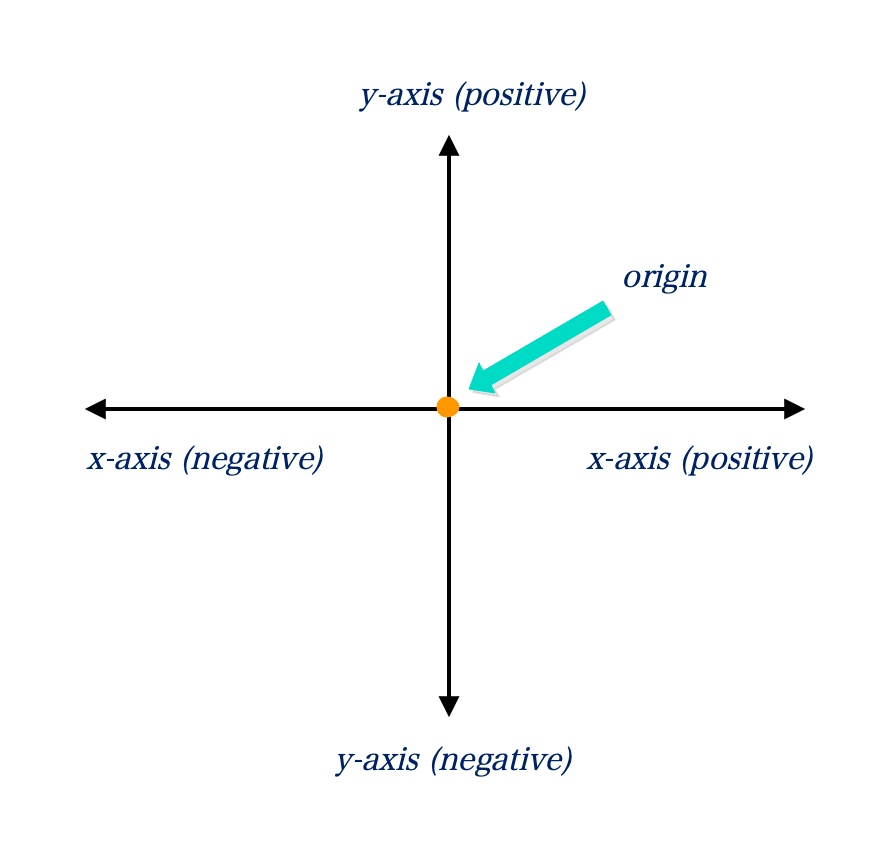
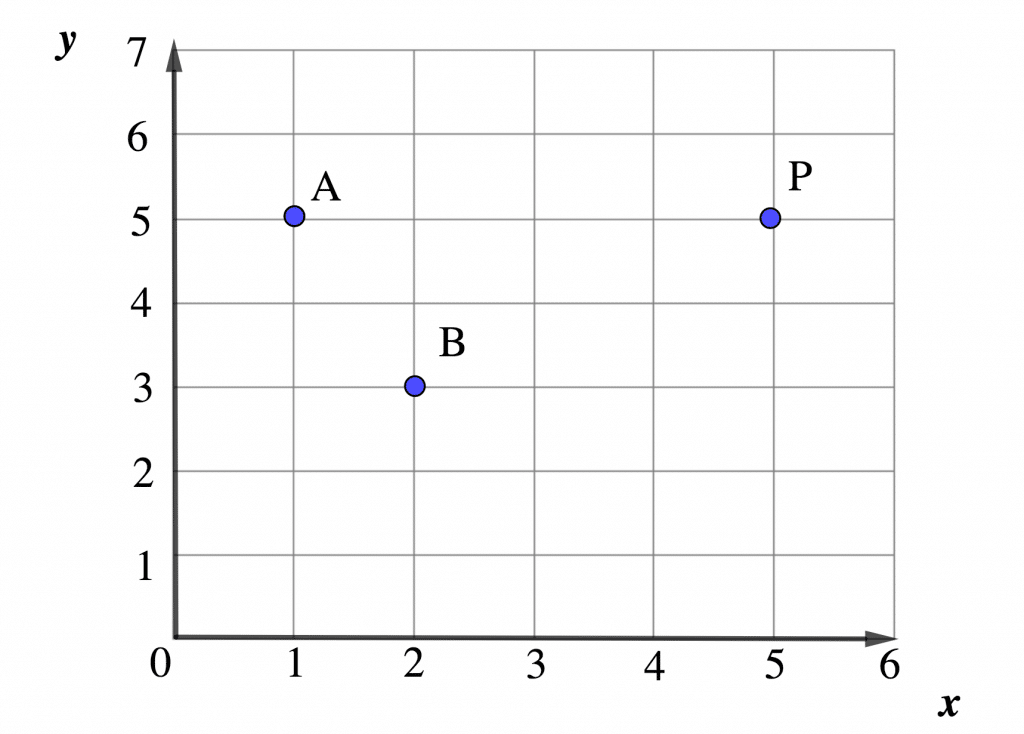
The plane x, y is called the Cartesian coordinate system P (x, y)
The x-coordinate is always written first followed by a comma and then the y-coordinate
Let’s consider the image above:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses