5. Fracture:
A fracture is a break, bend or crack in the bone of the body, It is a major injury to the bone.
Types of Fracture:
A. Green-stick Fracture:
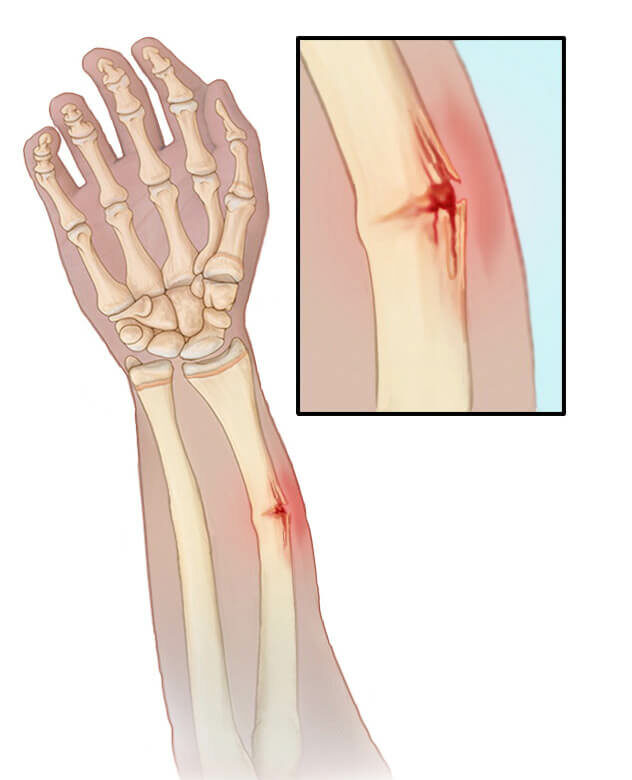
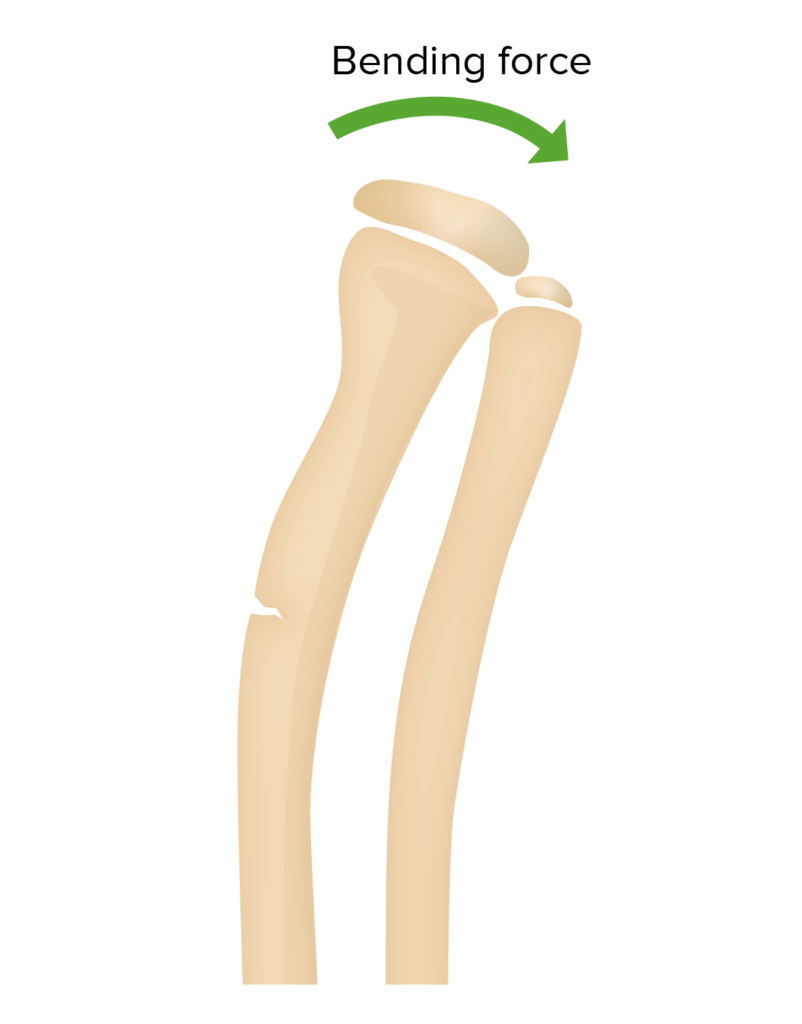
Green-stick fracture is common in children younger than 10 years of age. It is the bending of bones without the bones breaking.
B. Complicated Fracture:
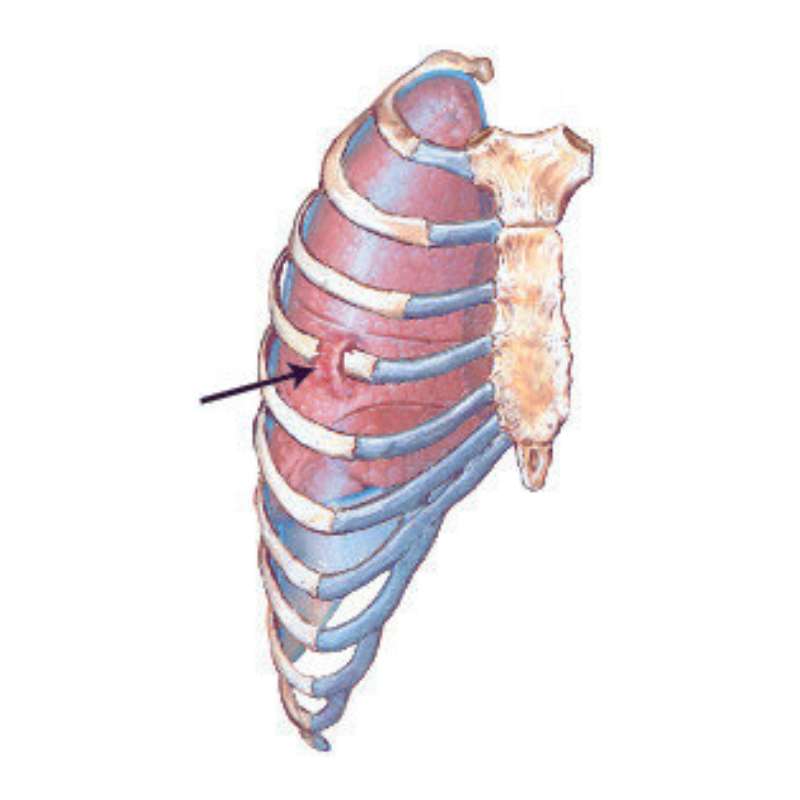
Complicated fracture is a type of fracture that involves injury to body structures surrounding the fracture, like blood vessels, liver, lungs, nerve or heart. It could result in damage to the body structure or organ.
C. Multiple Fractures:
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!



Responses