Power is dissipated in the resistor in an a.c circuit
P = IV = I2 R
Power dissipation in inductor and capacitor is zero
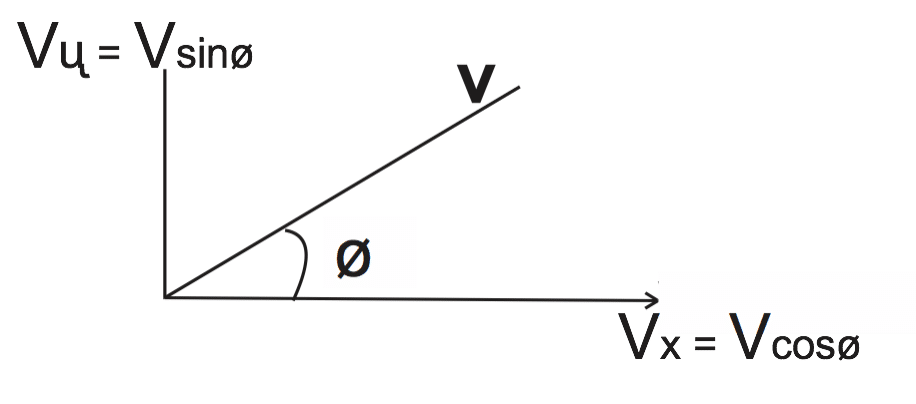
Vsinφ is the voltage across total inductance and capacitance where power is zero, the horizontal component voltage is in phase with the current I, gives the useful power in the circuit, Cosø. Cosø is therefore called the power factor
Therefore, P = IVcosø
cosø = \( \frac {R}{z} = \frac{V_R}{V}\)
Example
An electric cooker of 150Ω uses an a.c current of peak value 5.0A. What is the power dissipated?
Solution
Irms = \( \frac{I_0}{\sqrt{2}}\) = 0.707 I0 = 0.707 x 5 = 3.5A
Power dissipated, P = \( \scriptsize I_{rms}^2 R \)
= (3.5)2 x 150
= 1837.5W



Responses