i. Compton Effect: When x-ray of known wavelength is allowed to collide with a stationary electron, the x-ray transfers energyEnergy is the ability to do work. Energy exists in several forms such as heat, kinetic or mechanical energy, light, potential energy, and electrical energy. Units of Energy: The SI unit... More and momentum to the electron. The energy lost by x-ray is equal to the energy gained by the electron, hence energy and momentum are conserved. In this way, matter behaves as a particle.
ii. Photoelectric Emission: When light photon hits a surface, it gives up energy to the electrons on the surface. If the energy of the incident photon is sufficient to force electrons from the electrostatic force binding the electron to the surface, electrons are removed and extra energy moves them away from the surface.
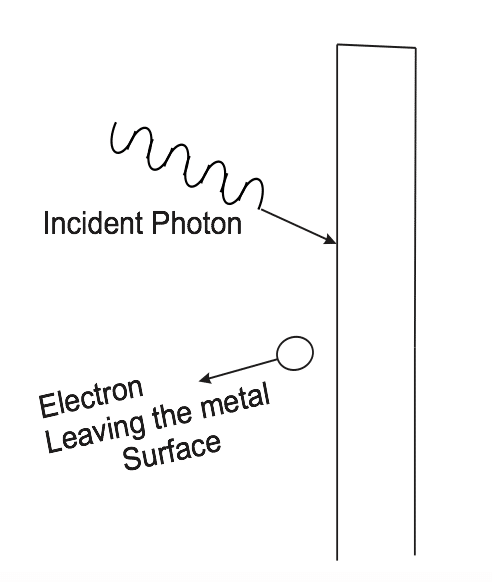
iii. Light as a Photon: Light exist as small packets called photons or discrete packets called quanta.
iv. Wave Nature of Matter
According to De Broglie
λ =\( \frac {h}{mv} = \frac{h}{p} \)
Particles such as electrons, protons and neutrons exhibit wave properties such as diffraction and interference.
The k.e is related to momentum by:
Ek = \( \frac{1}{2} \scriptsize mv^2\) = eV
∴ \( \frac {p^2}{2m} \) = eV
P2 = 2meV
P = \( \scriptsize \sqrt {2mev} \)
According to De Broglie,
λ = \( \frac{h}{p} = \frac{h}{\sqrt {2mev}}\)
Example
An electron of mass 9.1×10-31kg is accelerated by a p.d of 4000v. Find
(i) The wavelength of the wave in relation to electron
(ii) Velocity of the electron. h = 6.6 x 10-34Js, m = 9.1 x 10-31kg, e = 1.6 x 10-19c
Solution
(i) λ = \( \frac{h}{\sqrt {2mev}}\)
= \( \frac{6.6 \times 10^{-34}}{\sqrt {2\; \times \; 9.1 \times 10^{-31} \; \times \; 9.6 \times 10^{-19}\; \times \; 4000}}\)
= 1.34×1011m
(ii) eV = \( \frac{1}{2} \scriptsize mv^2\)
= \( \scriptsize 1.6 \times 10^{-19} \; \times \; 4000 = \frac{1}{2} \; \times 9.1 \times 10^{-19} \; \times \; V^2 \)
V2 =\( \frac{1.6 \times 10^{-19} \; \times 4000 \; \times \; 2 }{9.1 \times 10^{-19}} \)
= 1.40×1015ms-1



Great lesson
nice one