Topic Content:
- The Shapes of Atomic Orbitals
Electrons orbit the nucleus in circles called the energyEnergy is the ability to do work. Energy exists in several forms such as heat, kinetic or mechanical energy, light, potential energy, and electrical energy. Units of Energy: The SI unit... More levels (n)
Inside the energy levels are sublevels s, p, d, f
inside the sub-levels are orbitals.
Energy level ⇒ sublevel ⇒ orbital
An orbital is defined as the region or space in which an electron in a given energy level is most likely to be found. An orbital is also a region where there is a probability of finding an electron.
| n | Sublevels inside |
| 1 | s |
| 2 | s, p |
| 3 | s, p, d |
| 4 | s, p, d, f |
| Sublevel | Number of orbitals |
| s | 1 |
| s, p | 3 |
| s, p, d | 5 |
| s, p, d, f | 7 |
Shapes of s and p Orbitals:
The s Orbital:
The s-sublevel has only one orbital. It is called s-orbital. The s electrons move about to produce the effect of a spherical cloud around the nucleus. Thus, s orbital is spherical in shape.
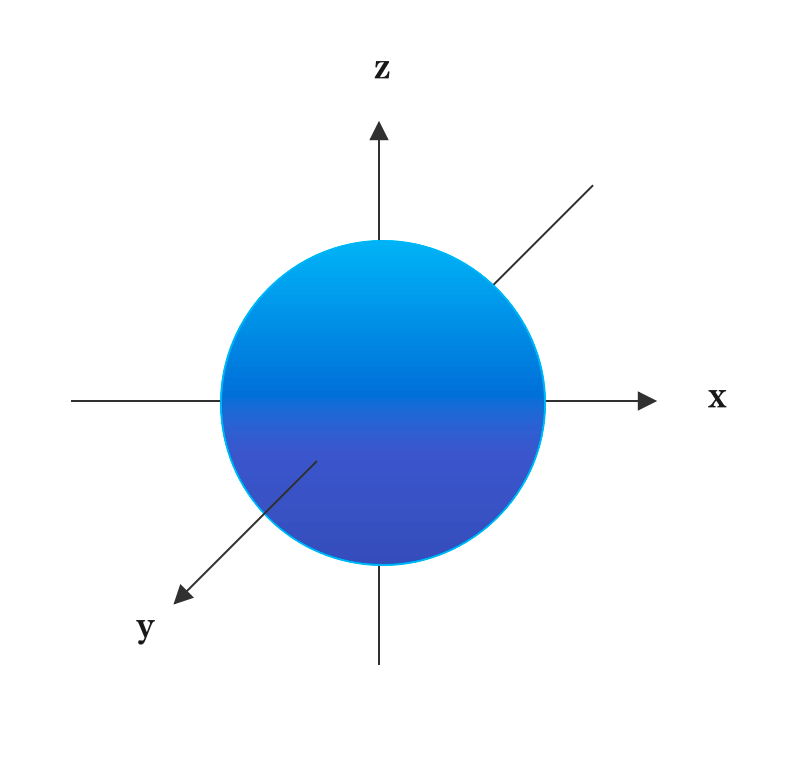
The p orbital
The p electrons move about three axes x, y, and z that are at right angles to each other. Each p-orbital has a dumbbell shape. They are distinguished from each other by the designation Px, Py, Pz according to the axis.
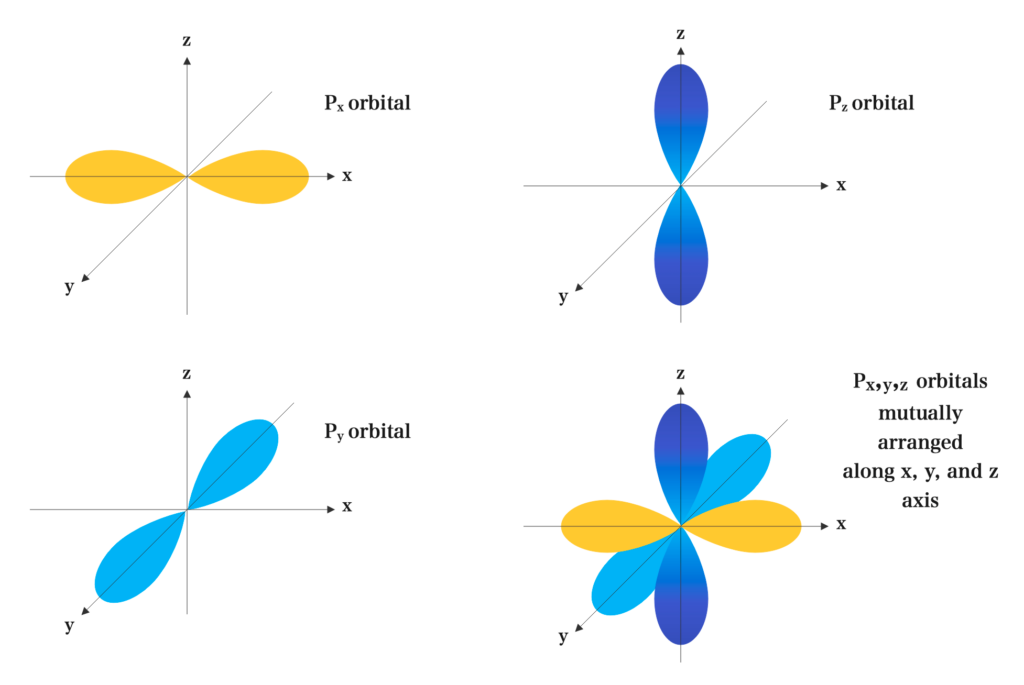



Responses