Topic Content:
- Theory Questions & Answers – Kingdom Fungi & Kingdom Plantae
Theory Questions – Kingdom Fungi & Kingdom Plantae:
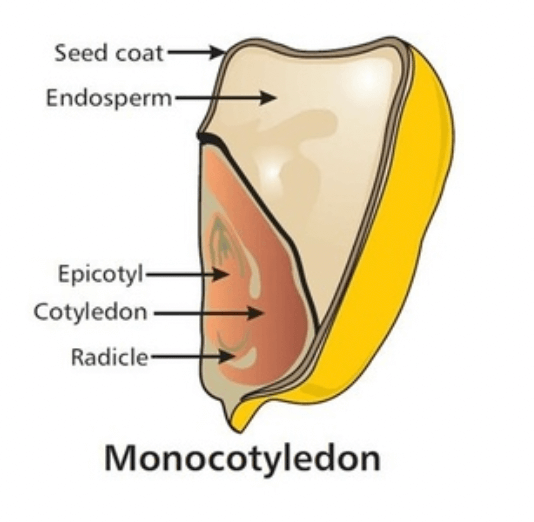
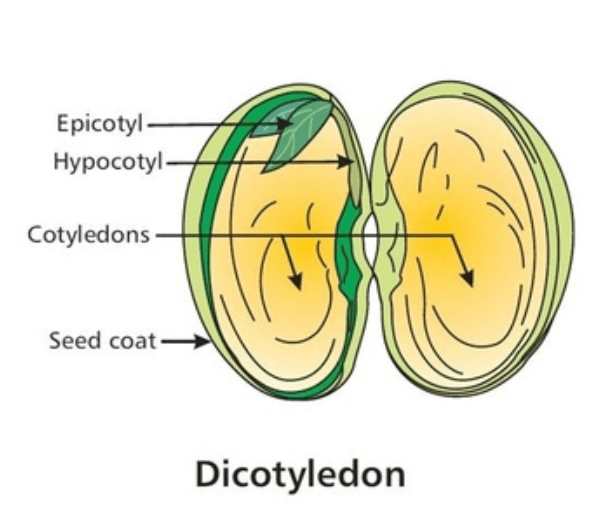
1a. List five characteristics of the kingdom fungi
b. State the differences between bacteria and fungi
c. State five economic importance of fungi
You are viewing an excerpt of this Topic. Subscribe Now to get Full Access to ALL this Subject's Topics and Quizzes for this Term!
Click on the button "Subscribe Now" below for Full Access!
Subscribe Now
Note: If you have Already Subscribed and you are seeing this message, it means you are logged out. Please Log In using the Login Button Below to Carry on Studying!







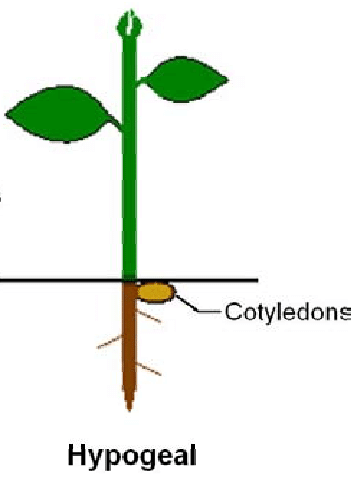
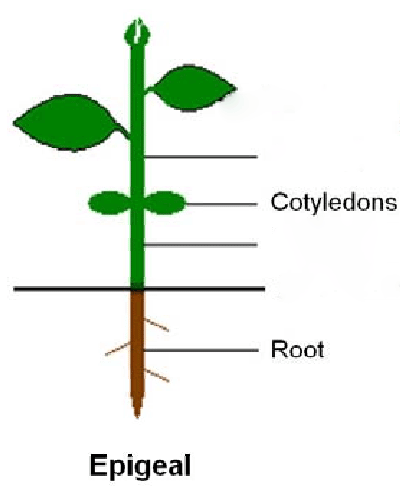
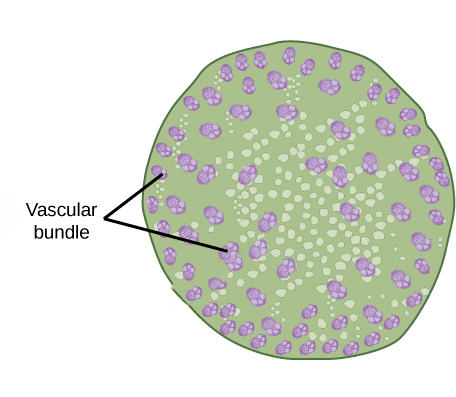
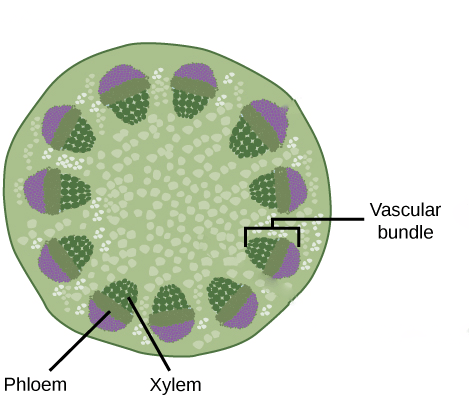
Responses