Topic Content:
- Meaning of Science
- Meaning of Scientific Method
- Scientific Method Steps
- Summary

What is Science?
Science is the systematic process of making enquiries about the living and non-living things in our environment.
Science is all about finding out things. Biology employs the method of science in enquiry which begins with observation.
What is Scientific Method?
The Scientific method is a process in which scientists try to investigate, verify, or construct an accurate and reliable version of any natural phenomena.
This is done by creating a structure for the purpose of scientific inquiry and analysing the results scientifically to come to a conclusion that either supports or contradicts the observation made at the beginning.
Flow chart:
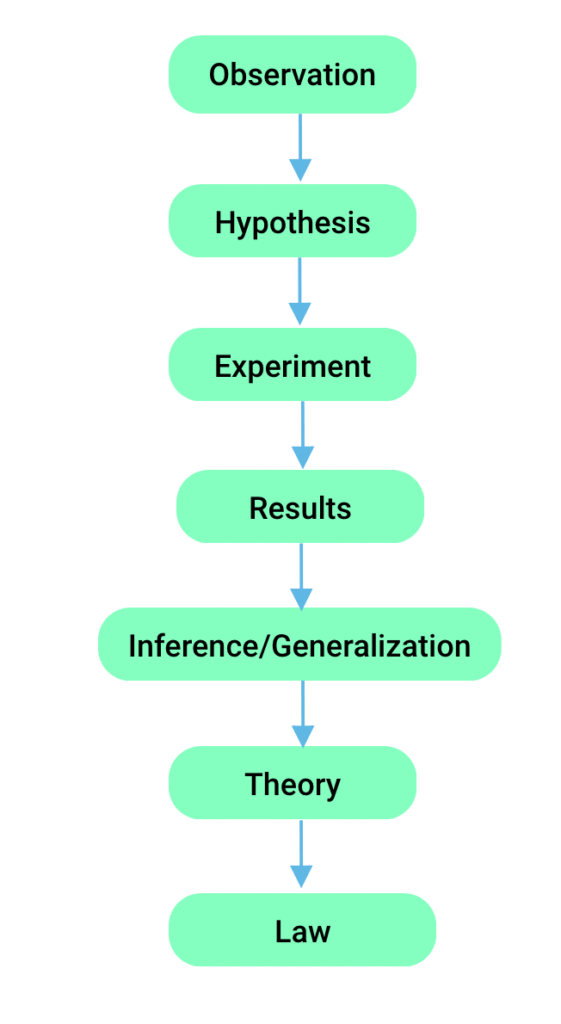
Scientific Method Steps:
The following steps must be taken in carrying out a project or study in science.
I. Observation
II. Identifying a problem
III. Hypothesis
IV. Experimentation
V. Collation & Interpretation of findings & date
VI. Conclusion
VII. Generalization and Theorizing
I. Observation:
This means looking at something carefully and critically with a view to finding an answer to a problem or question. The senses (i.e. sight, taste, hearing, touch, smell) are used in making observations. This leads to the formation of a hypothesis or a tentative answer that can be
tested.
II. Hypothesis:
This is a tentative answer or guess which can be tested.
III. Experimentation:
Experiments involve measurements and counting. They usually have control. Control is part of an experiment that proves that the changes observed in an experiment are due to the factors being considered. It gives the investigator a high degree of confidence in his result and conclusion. It eliminates bias or doubt.
The control experiment is placed under normal conditions while in the test experiment, all the factors are also present except the factor being considered which is either eliminated or varied.
IV, V, VI. Collation, Conclusions, Generalization and Theorizing:
Results from an experiment are collated and conclusions are drawn. When other scientists repeat the experiment and get the same result, it becomes a theory. When a theory has been tested and found to be consistently true, it is accepted as a law or principle. New discoveries improved technology and continual experimentation can also lead to the modification of existing laws.
Summary of Main Stages:
a. Observe the natural phenomenon
b. Note the pattern of events and identify a problem
c. Formulate and state hypothesis (scientific guesses)
d. Design and carry out experiments to test the hypothesis



Wow I love it
Lovely
Understood
Wonderful